
Gen info
Portulaca comes from the Latin portula, meaning "little gate," for the top of the seed capsule that opens like a gate.
 Botany Botany
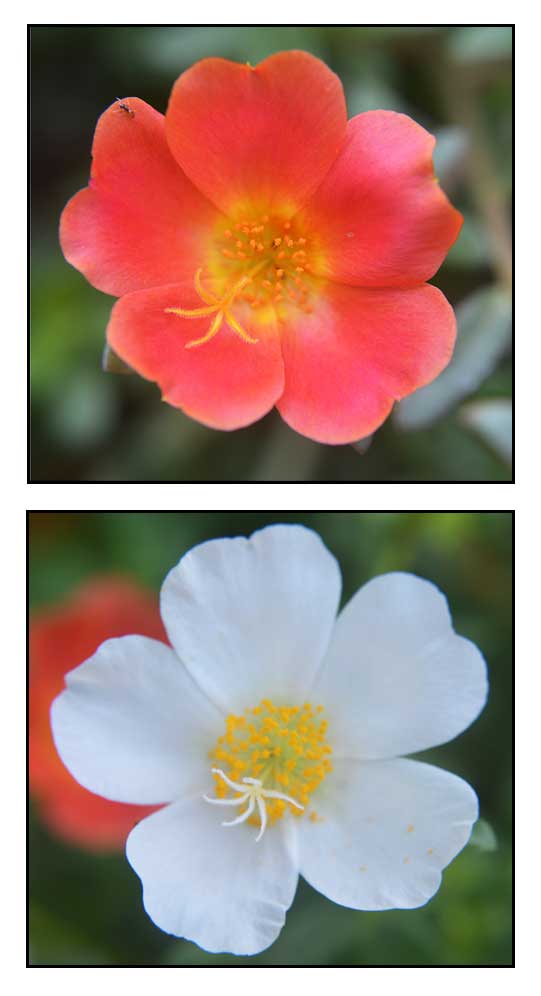
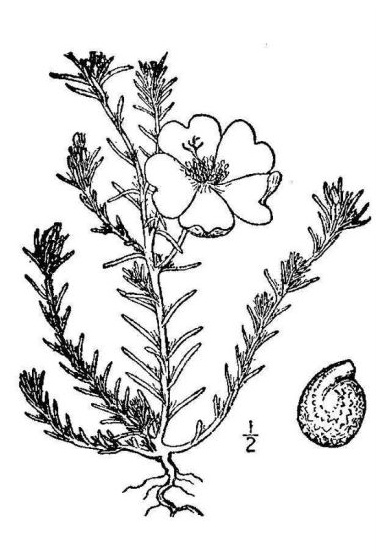
Portulaca grandiflora is a low, fleshy, trailing perennial herb attaining a height of 15 to 30 centimeters. . Stems are slender and terete, prostrate or ascending, with hairy joints. Leaves are small, thick and fleshy, clustered, up to 2 centimeters long, alternate or in small clusters. Flowers are showy, terminal, up t 3 centimeters across, subtended by clustered leaves. Petals are five, red, white, yellow or pink, opening in mid-morning and closing by mid-afternoon. Fruit is a small capsule, releasing seeds when ripe.
Distribution
- Introduced.
-
Widely distributed in the Philippines.
- Popular use as ground cover.
- Native range is Peru to Brazil and Argentina.
Constituents
- Petals have yielded free betalamic acid, together with betaxanthins. Tyrosine and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) are precursors of betalain biosynthesis. (3)
- Total ash and acid-insoluble ash contents were not more than 19% and 1% w/w, respectively. (6)
- Phytochemical screening of aerial parts yielded sterols, carotenoids, polyphenolic acids, flavonoids, polysaccharides, reducing agents and triterpenoids. (see study below) (12)
Properties
- Flowers only open in bright sunlight, not with overcase skies or at night.
-
Entire plant considered depuratiive.
-
Studies have shown antioxidant, lipid-regulating, phytoremediative, antibacterial, antidiabetic, nephroprotective properties.
Parts used
Flowers, leaves, flowers, juice.
 Uses Uses
Edibility
- Leaves are edible, raw or cooked.
- Seeds, raw or cooked; can be ground into a powder and used in soups or added to cereals.
- Root is cooked.
Folkloric
- No reported folkloric medicinal use in the Philippines.
- Used for the treatment of cirrhosis of the liver, pharyngeal pain and swelling.
- Leaves used for scurvy.
- Fresh juice of leaves and stems applied to snake and insect bites, burns, scalds, and eczema. (4)
- In Chinese medicine, used to treat various tumors. One of the ingredients of the Chinese herbal medicine, Tumoclear (Kang zhong pian) formulated for tumor and cancer care.
- In Thai medicine, aerial parts used for treatment of sore throat, skin rash and detoxification.
- Leaves and flowers worn around the neck to relieve muscle spasms and neck stiffness.
Others
- Superstitions: Flowers and leaves placed on child's bed to drive evil spirits away. (9)
Studies
• Chronic Toxicity Study: Study evaluated the toxic effects of Portulaca grandiflora aqueous extract in male and female Wistar rats for 6 months. The water extract at given doses of 10, 100, and 1000 mg/k per day did not induce any detrimental effect in rats. (2)
• Phytoremediation Potential : Study showed wild and tissue cultured plants of P. grandiflora were able to decolorize sulfonated diazo dye Navy Blue HE2R up to 98% in 40 h. The significant induction in the activities of lignin peroxidase, tyrosinase and DCIP reductase was observed in roots during dye decolorization. Phytotoxicity study showed reduction in toxicity due to metabolites formed after dye degradation. (5)
• Safety Study / Phase 1 Trial / Healthy Human Volunteers: A phase 1 clinical trial in 16 healthy volunteers investigated the safety of P. grandiflora, as well as preliminarily assess its efficacy on the immune system. The aqueous extract at 500 mg/day dose given to normal volunteers for 2 months was found to be safe. (7)
• Effect on Human Lymphocyte Activity: Study evaluated eight medicinal plants, including Portulaca grandiflora extract, for effects on lymphocyte function. All the extracts significantly stimulated human lymphocyte proliferative responses. Results suggest human lymphocyte stimulating activity and a potential for clinically modulating immune functions of the body. (8)
• Antioxidant / Lipid Regulating Effects / Betacyanin Extract: Study of a betacyanin extract of Portulaca grandiflora showed scavenging effects which superoxide anion, OH, and DPPH free radicals. The betacyanin extract significantly reduced total cholesterol, TG, LDL-C, Apo B. It also significantly decreased the atherosclerosis index suggesting an atherosclerosis preventive effect. (10)
• Portulene Acetal: A new clerodane diterpenoid was isolated as a minor constituent from P. grandiflora, a compound that might be significant in the biosynthesis and chemosystematics of constituents of the genus Portulaca. Its features provide clues for the biosynthesis of portulaca. (11)
• Antibacterial / Aerial Parts: Study of alcoholic extract of aerial parts showed varying degrees of inhibition against all bacterial strains tested, with more MIC for Pseudomonas aeruginosa followed by C. albicans. (see constituents above) (12)
• Fluoride Phytoremediation: Fluoride is one of the common environmental pollutant in soil and water. Study evaluated the possible role of P. grandiflora and B. oleracea plants to uptake and accumulate fluoride from water. The accumulation of fluoride was comparatively more in root than on leaf parts in both studied plants. Results showed both plants can clean fluoride contaminated water and presents a cost effective and ecofriendly alternative for in situ treatment of soil and water samples. (13)
• Prevention of Neuroinflammation or Neurodegenerative Diseases / Patent Application: Patent application made for an invention of a pharmaceutical composition and food composition containing Portulaca grandiflora or fraction as active ingredient for preventing, treating or ameliorating neuroinflammation or neurodegenerative diseases by inhibition of expression of NO, PGE2, iNOS, and/or COX-2 genes or protein. (16)
• Gold Nanoparticles / Leaf and Stem / Cytotoxicity Against Glioma Human Cancer Cells: Study on the synthesis of gold nanoparticles using leaf and stem extracts of green roof vegetation. The presence of proteins and polyphenols were responsible for the reduction and stabilization of gold nanoparticles. Study for antiproliferative effects using C6 glioma human cancer cells showed decreased viability of glioma cell lines up to 50%. (17)
• As Green Roof Vegetation / Phytoremediation: Appropriate rooftop vegetation may improve the quality of runoff from green roofs. Study evaluated P. grandiflora as a possible vegetation for green roofs. The plant accumulat3ed all metals viz. Al, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni, Pb, and Zn from metal-spiked green roof substrate. P. grandiflora showed potential to translocate all the examined metals with translocation factor greater than 1 for Al, Cu, Fe, and Zn, indicating hyperaccumulation property. (18)
• Antioxidant / Total Phenolic Content: Study evaluated various crude extracts from five different color varieties of P. grandiflora for in vitro antioxidant and total phenolic content. Total phenolic content ranged from 46.39 - 82.19 mg GAE/100 g, 36.72 - 56.45 mg GAE/100 g, and 41.46 - 85.70 mg GAE/100 g for methanolic, acetone and ethanolic extract, respectively. Antioxidant activity by DPPH assay ranged from 0.69 - 2.14 mg/mL, 1.40-4.38 mg gallic acid/g, and 7.32-29.21 mg ascorbic acid/g by IC50, GEAC, and AEAC, respectively. Highest antioxidant activity was observed in the acetone extract of the orange variety. (19)
• Antidiabetic Activity / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated the antidiabetic activity of ethanolic extract of whole aerial plant on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. Results showed significant reduction in blood glucose levels and elevation in body weight at oral dose of 200 and 400 mg/kg for 21 days. Glibenclamide was used as reference drug. (20)
• Effect on Diabetic Nephropathy / Leaves: Study evaluated the effect of leaves extract of Portulaca grandiflora in preventing nephropathy in alloxan-induced diabetic albino rats. Results showed significant reduction in levels of glucose, uric acid, creatinine, urea in diabetic rats. Study suggests the potential of P. grandiflora in minimizing complications of diabetic nephropathy by its antioxidant activity. (21)
Availability
- Wild-crafted.
- Ornamental cultivation.
- Seeds. mixed or double-flower variety, in the cybermarket.
|

![]()




 Botany
Botany Uses
Uses