Gen info
- Allium is a genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants with hundred of species, including the cultivated onion, garlic, scallion, shallot, leek, and chives. It is one of about 57 genera of flowering plants with more than 500 species. It is the largest genus in Amaryllidaceae, and also in the Alliaceae in classification systems where the family is recognized as separate. (73)
 - The genus was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
- The genus was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
- Etymology: The generic name Allium is Latin for garlic, and the type species is Allium sativum, which means "cultivated garlic".
- Taste and odor: Plants in the genus produce chemical compounds, mostly derived from cysteine sulfoxides that give the characteristic onion or garlic taste and odor. The characteristic Allium flavor depends on the sulfate content of the soil, and in the rare occurrence of sulfur-free conditions, Allium species completely lose their usual pungency. (73)
- It has a history of culinary and medicinal use for several thousand year. As a medicinal remedy, Ebers Papyrus (1550 BC) attributed antitumoral effects to the plant. (77)
- The largest producers is China, which produced 73% of the world's supply in 2021. (74)
- Bawang belongs to Secretary of Health Juan Flavier's 1992 brochure of 10 medicinal plants (akapulko, ampalaya, bawang, bayabas, lagundi, niyog-niyogan, pansit-pansitan, sambong, tsaang-gubat, yerba buena), which provided underpinning and roots for the 1977 TAMA (Traditional and Alternative Medicine Act).
Botany
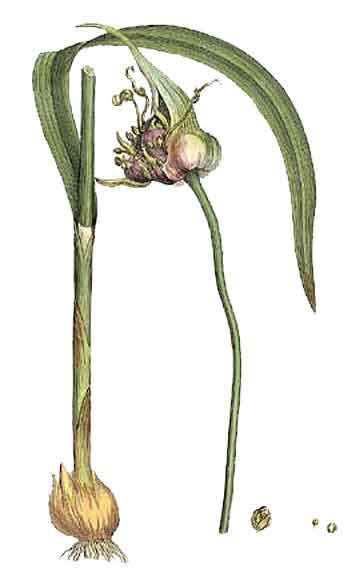
• Bawang is a low herb, 30 to 60 centimeters high. True stem is much reduced. Bulbs
are broadly ovoid, 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter, consisting of several, densely
crowded, angular and truncated tubers. Leaves are linear and flat.
Umbels are globose, many flowered. Sepals are oblong, greenish white,
slightly tinged with purple. Stamens are not exerted from the perianth.
• Foliage: Broadly linear-lanceolate, scattered along the pesudostem; leaf-blade linear oblong, apex acute. Stems: Real stem very short, flattened, forming a disk at the base of the bulb. Bulb depressed globular to ovoid, usually consisting of several bulbels (tiny secondary bulb) covered with protective bulb-coat leaves, whitish to purplish. Pseudostem formed by the sheathing base of successive leaves. Flowers: Inflorescence a sub-spherical umbel with many bulblets and few flowers, protected by a membranous spathe. (81)
Distribution
- Cultivated, not naturalized.
-
Extensively
grown in Batangas, Nueva Ecija, Ilocos Norte, Mindoro, and Cotobato.
- A native of southern Europe.
- Widely cultivated in most parts of the world.
Constituents
• Garlic contains at least 33 sulfur compounds, several enzymes, 17 amino acids, and minerals. The sulfur compounds are responsible for the pungent odor and many of its medicinal effects.
• Saponins; tannins; sulfurous compounds;
prostaglandins; alkaloids; volatile oils; allicin (bulb).
 • The anthelmintic property is due to allyl disulphide content.
• The anthelmintic property is due to allyl disulphide content.
• The most important chemical constituents are the
cysteine sulfoxides (alliin) and the nonvolatile glutamylcysteine
peptides which make up more than 82% of the sulfur content of garlic.
Allicin, ajoenes and sulfides are degradation products of alliin.
• Some of garlic's effect is attributed to alicin,
its active ingredient, which is converted to ajoene, allyl sulfides and vinyldithiins.
• Allicin (dially thiosulfinate or dially disulfide) is generated only when the garlic is crushed or cut, which activates the enzyme allinase which metabolizes alliin to allicin.
• Aged garlic products lack allicin, but may have activity due to the presence of S-allycysteine.
• Bulb: allicin; volatile oil, 0.9% - allyl disulfide, allypropyl disulfide;
inulin; protein; fat, 1.3%; carbohydrates, 0.2%; ash, 9.4%; choline,
0.7%; myrosinase.
• Leaves: Protein, i.2%; fat, 0.5%; sulfides.
• Proximate analysis of bulb extract g/100g yielded carbohydrate (66.0%), protein (16.23%), fats (2.44%), crude fiber (03.96%), moisture (5.52%) and ash (05.85%). Mineral analysis yielded calcium (23.40%), [potassium (10.95%), magnesium (3.90%), zinc (0.44%), phosphorus (9.85%), iron (5.20%), and copper (0.05%). (54)
- Nutrient value per 100g
yields: 623 kkJ (149kcal), carbohydrates 33.06 g, sugars 1 g, dietary fiber 2.1 g, protein 6.36 g; (Vitamins) thiamine/B1 0.2 mg riboflavin/B2 0.11 mg, niacin/B3 0.7 mg, pantothenic acid/B5 0.596 mg, vitamin B6 1.235 g, folate/B9 3 µg, vitamin C 31.2 mg; (Minerals) calcium 181 mg, iron 1.7 mg, magnesium 25 mg, manganese 1.672 mg, phosphorus 153 mg, potassium 401 mg, sodium 17 mg, zinc 1,16 mg. (USDA Nutrient Database) (66)
Properties
• Considered antibacterial, anthelmintic, antimycotic, antiviral,
antispasmodic, diaphoretic, expectorant, fibrinolytic, hypotensive,
promoting leucocytosis, lipid lowering and platelet aggregation inhibition.
- Studies have suggested antimicrobial,
antihypertensive, antihyperlipidemic, anticancer, chemopreventive, antidiabetic, hepatoprotective, antithrombotic, analgesic, virucidal, nephroprotective, anti-H. pylori, repellent, wound healing, antioxidant properties.
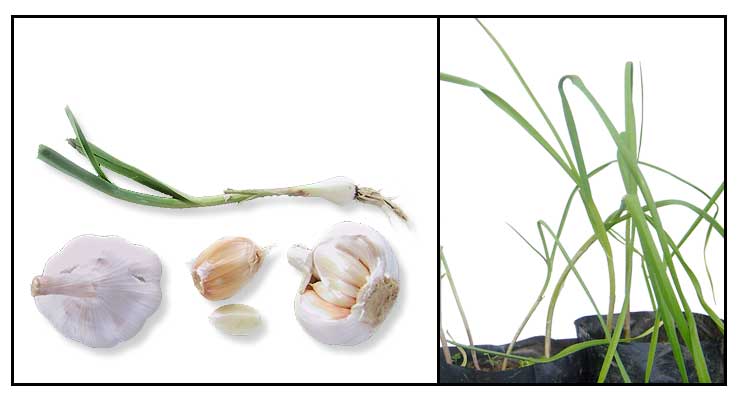
Parts
utilized
Bulbs: Features prominently as a condiment
and flavor in Filipino cuisine.
Herbalists, with concerns that cooking diminishes medicinal potency,
recommends eating raw garlic cloves.
 Uses
Uses
Edibility
- Widely used by Filipinos for flavoring dishes.
Folkloric
- In the Philippines, bulbs used for hypertension. Also used as diuretic, and eaten fresh or burned for coughs in children.
-
Arthritis, rheumatism, toothaches: Crush
several cloves and rub on affected areas.
- Crush clove applied to both temples as poultice for headache.
- Crush garlic or cut clove crosswise and rub directly
to areas of insect bites.
- Decoction of leaves and bulbs for fever and as hypotensive, carminative,
expectorant, and antihelmintic.
- Juice from freshly crushed garlic used for colds, cough, sore throat,
hoarseness, asthma and bronchitis.
- Decoction use for tonsillitis.
- Steam inhalation of chopped garlic and a
teaspoon of vinegar in boiling water used for nasal congestion.
- Fresh garlic has been used as a complement to INH therapy for tuberculosis.
In Mexico, fresh bulb is eaten as a preventive for tuberculosis.
- In India, garlic juice diluted in water, applied externally to prevent hair from turning gray.
- Diluted juice used for earaches and deafness.
- In the Antilles, used as vermifuge.
- Also used for menstrual cramps.
- Used for digestive problems and gastrointestinal spasms.
- Infusion of a peeled broiled clove used for gas pains.
- Juice of bulb with common salt applied to bruises and sprains; also used for neuralgia and earache.
- Rubbed over ringworm for soothing effect.
- In WWI, fresh raw juice was used as antiseptic for control of wound suppuration.
Studies
• Antibacterial, antifungal,
antiparasitic: Topically, ajoene 0.4% cream, has been found 70% effective
in certain dermatologic fungal infections. A 0.6% gel was effective
in tinea corporis and tinea cruris.
• Anticandidal: Study on the mode of action of aqueous garlic extract (AGE) against Candida albicans showed garlic treatment affected the structure and integrity of the outer surface of the yeast cells. Growth was affected in a number of ways: decreased total lipid content, higher phosphatidylserines and lower phosphatidylcholines, and decrease oxygen consumption of AGE-treated C. albicans. AGE exerts its effect by oxidation of thiol groups causing enzyme inactivation and subsequent microbial growth inhibition.
• Antihypertensive: Studies suggest a beneficial
antihypertensive effect but blood-lowering effects probably not dramatic.
Other studies show a vascular benefit through improvement of aortic
elasticity and possible slowing of the rate of atherosclerosis progression.
• Antihyperlipidemia / Antioxidant:Controversial, but probably has
beneficial effect on serum cholesterol and LDL levels. Some studies
have shown a 4% to 12% lowering of total cholesterol. It seems to
have no effect on high density lipoprotein (HDL).
• Hypocholesterolemic / Fresh Bulbs: Study of feeding
of fresh garlic bulbs to induced-hypercholesterolemic rats showed
decrease in total and LDL cholesterol and increase in HDL levels. (6)
• Lipid Profile Benefits:
Study concluded that garlic extracts may have a beneficial effect
on blood lipid profile and antioxidant status. (7) Study evaluated the effect of Allium sativum on experimentally induced hyperlipidemia in guinea pigs. Aqueous and alcoholic extracts showed significant hypolipidemic activity with significant reduction in triglycerides, LDLc, VLDLc and atherogenic index. (36)
• Anti-cancer / Chemoprotective: Possible anticarcinogenic properties, specifically colon,
stomach and prostate cancers— in stomach cancers, probably through
its inhibitory effect on H. pylori. In epidemiologic studies on stomach
and colorectal cancer prevention, the garlic use was 3.5 grams to
30 grams of fresh or cooked garlic per week. • Studies provide ample evidence for a role of garlic in cancer prevention. The tumor inhibition may be through compounds like organosulfur in garlic.
• Effect on Salivary Gland Tumorigenesis: Study showed garlic may have an adjuvant effect on various defense mechanisms against -induced carcinogenesis in sub-maxillary salivary glands of rat through increased availability or utilization of beta-carotene. (10)
• Hepatoprotective / Hematologic Effects:
Study results on female Wistar rats suggest garlic and
vitamin C have some hepatoprotective and hematological effects. (3)
• Antidiabetic:
Study evaluated the effect of increasing doses of A. sativum aqueous extracts on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Results showed promising hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activity. Glibenclamide was used as standard. (29) Study results of ethanolic extracts of AS in normal and
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats suggest that A. sativum can be
considered an excellent candidate for future studies on diabetes mellitus.
• Sperm Immobilization Activity :
Study of crude extract of A. sativum bulb showed spermicidal
activity in vitro. (8)
• Hepatopulmonary Syndrome Treatment: A trial showed garlic may improve oxygenation and symptoms in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. (9)
• Anti-Thrombotic Activity : Study of extracts of Allium sativum and Vernonia amygdalina showed both extracts offered protection against thrombosis produced by an intravenous injection of ADP and adrenalin, with A sativum showing the stronger activity. (11)
• Diallyl Sulfide / Anti-Cancer: Study showed diallyl sulfide, a thioether found naturally in garlic, when given by gavage to mice, inhibited by 74% the incidence of colorectal adenocarcinoma induced by 1,2-dimethyl-hydrazine. (12)
• Cardiovascular Benefits: Garlic is an ideal herb with its several cardiovascular benefits: blood pressure lowering, antihyperlipidemic effects, platelet inhibition and fibrinolytic effects, antioxidant and antiatherosclerotic effects. (14)
• Antibacterial / Anti-Staph aureus: Study of an aqueous extract of Allium sativum showed concentration-dependent antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus. (15)
• Antitumorigenesis: Study showed garlic oil may have an adjuvant effect on host defense mechanisms against DMBA-induced carcinogenesis in sub-maxillary glands of rat through increased availability and utilization of beta-carotene. (16)
• Antimicrobial / Crude Juices: Study evaluated the antimicrobial activity of crude juices of Allium ascalonicum, Allium cepa, and Allium sativum. Results showed strong antibiotic properties, and the complete absence of development of resistance from juices of Allium species merit consideration. (17)
• Antioxidant: In a study using DPPH scavenging method, raw garlic extract showed a color change from deep violet to yellow, indicating antioxidant activity. (18)
• Essential Oil / Antibacterial / Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: Essential oil extract from Allium sativum bulbs showed inhibitory activity on growth of over 50% of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains tested. (19)
• Antibacterial / Garlic and Ginger Comparative Study: In a study comparing the antimicrobial potency of various extracts of garlic and ginger, results showed all the bacterial strains to be most susceptible to garlic aqueous extract while showing poor susceptibility to the ginger aqueous extract. (21)
• Chemoprevention: Experimental studies provide compelling evidence that garlic and its organic allyl sulfur components are effective inhibitors of tumor growth. (22)
• Anti-Ulcer: Study showed the protective role of raw Nigelia sativa, garlic, and onion against ethanol-induced gastric ulcers and gastric acid secretion. Raw or boiled Nigella sativa, garlic or onion significantly inhibited histamine stimulated acid secretion. Raw Nigella sativa and garlic showed a decrease in ulcer index. Boiling reduced the potency of garlic and onion. (23)
• Allyl Alcohol and Garlic in Oxidative Stress Effects on C. Albicans: Study evaluated on the effects of purified constituents, in particular, allyl alcohol, a metabolic product that accumulates after titration of garlic cloves on anticandidal activities. Typical changes of oxidative stress were observed—NADH oxidation and glutathione depletion, and increased reactive oxygen species.
(24)
• Antimicrobial Effects with Combined Extracts: Study evaluated the in vitro antimicrobial effects of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of garlic (A. sativum), ginger (Zingiber officinale) and lime (Citrus aurantifolia) against S. aureus, Bacillus spp., E. coli and Salmonella spp. The aqueous and ethanolic extracts of garlic and ginger did not inhibit any of the test organisms. The highest inhibition zone was seen with combination of extracts on Staphylococcus aureus. (25)
• Antibacterial Against Multiple-Drug Resistant Pathogens / Cloves: Ethanol extracts of cloves of garlic and rhizomes of ginger showed effective antibacterial activity against multi-drug resistant clinical pathogens. The highest inhibition zone observed with garlic was against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. (26)
• Effect on Systolic and Diastolic Pressure in Essential Hypertension: Study evaluated the effect of garlic on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. Study showed a significant decrease in both systolic and diastolic pressure in a dose- and duration-dependent manner, when compared to atenolol and placebo. (27)
• Improved Diabetic Control with Garlic Supplementation: Study evaluated the potential effect of garlic in T2DM with the addition of garlic tablets to standard antidiabetic therapy. Results showed the combination of garlic with typical antidiabetic remedy improved glycemic control in addition to an antihyperlipidemic activity. (28)
• Anthelmintic: An alcoholic extract of bulb of A. sativum has shown moderate in vitro anthelmintic activity against human Ascaris lumbricoides. (20) Study evaluated methanol extracts of various plant materials of ethnoveterinary importance in Pakistan, including A. sativum, for in vitro anthelmintic activity. All the studied plants showed anthelmintic activity. (31)
• Analgesic / Antinociceptive: Study evaluated the analgesic and anti-nociceptive effects of Allium sativum powder in animal models. Results showed the ASP to be effective in both non-narcotic and narcotic models of nociception, suggesting possible peripheral and central mechanisms as well as peripheral pathways through inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. (30)
• Immune System Enhancement / Black Garlic: Study evaluated black garlic—created from ordinary fresh garlic—for antitumor activity. Heat extracts of black garlic were rich in S-allyl-L-cysteine (SAC) and enforced anti-tumor activity with a 50% cure rate of BALB/c mouse fibrosarcoma. The black garlic enhanced cellular immunity by raising the activity of NK (natural killer cell) cells which may play a critical role in eradication of tumor cells inn vivo. There was also generation of cytokines of NO, IFN-y, IL-2, and TNF-α from the extract-treated mouse spleen cells. (32)
• Antihypertensive : Study evaluated the cardiovascular effects of aqueous extracts of garlic on normotensive and hypertensive rats using the two-kidney one clip model. Aqueous garlic extracts caused a decrease in blood pressure and bradycardia by direct mechanism not involving the cholinergic pathway in normotensive and 2K1C rats, suggesting a likely peripheral hypotensive mechanism. (33)
• Effect on the Pharmacokinetic of Metformin / Herb-Drug Interaction: Study evaluated the pharmacokinetic interactions of Metformin with Allium sativum. Allium sativum altered the pharmacokinetics of Metformin in rats, increasing bioavailability by significantly increasing its Cmax and AUC0-12hr and a slight increase in t1/2. (34) Study evaluated the effect of garlic on metformin in STZ-induced diabetic rats.
• Effect on Liver Glycogen Deposition and Gonadal Protein Metabolism: Study evaluated the effect of garlic extract on glycogen deposition in the liver and protein metabolism in gonads of female albino rats. Results showed a significant increase in glycogen and protein level on low and medium dose of garlic extract, with a significant decrease in glycogen level with high dose of extract. The quantity of protein depends on rate of protein synthesis or on rate of degradation. (35)
• Pharmacodynamic Interaction with Cilostazol in Diabetic Patients: Garlic is known to have antiplatelet properties. Garlic showed significant inhibition of platelet aggregation. Cilostazol showed significant inhibition at all three time points tested. In the randomized, open label, placebo-controlled, crossover study of type II diabetes patients, coadministration of aged garlic extract and cilostazol did not produce any significant change in the antiplatelet activity of the individual drugs. (38)
• Virucidal: Garlic has been shown to have antiviral activity. Study identified garlic associated compounds: diallyl thiosulfinate (allicin), allyl methyl thiosulfinate, methyl allyl thiosulfinate, ajoene, alliin, deoxyalliin, diallyl disulfide, and diallyl trisulfide. Activity was determined against selected viruses including, herpes simplex virus type 1, herpes simplex virus type 2, parainfluenza virus type 3, vaccinia virus, vesicular stomatitis virus, and human rhinovirus type 2. Virucidal activity was: ajoene > allicin > allyl methyl thiosulfinate > methyl allyl thiosulfinate. Results indicate virucidal activity and cytotoxicity may depend upon the viral envelope and cell membrane, respectively. (39)
• Hepatoprotective / Paracetamol Induced Liver Damage: Study showed administration of A. sativum extracts protected against paracetamol liver damage in rats. (40)
• Nephroprotective / Cisplatin Toxicity: Study evaluated the in vivo antioxidant and nephroprotective potential of ethanolic extract of garlic against cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar male rats. Cisplatin induction decreased renal antioxidants with associated increase in kidney weight, lipid peroxidation and serum kidney markers. Treatment exhibited a protective effect as evidenced by boosting of antioxidant levels and markers reverting back to near normalcy. (41)
• Antibacterial / Anti-Pseudomonas / Anti-Staph: Study evaluated the effect of crude preparation of garlic on clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Results showed the targeting of bacterial cell wall and bacteriolytic action of the extract. The extract appeared to interfere with DNA and RNA synthesis. (42)
• Effect on Systolic Blood Pressure / Pilot Study: Pilot study showed individuals with blood pressures on the lower side are more likely to consume more garlic in their diets. Findings were statistically significant for systolic blood pressure only. The average garlic use was 134 grams per month; 67 % of use was cooked in foods while the rest consumed it in raw form or in pickles. (43)
• Processed Black Garlic / Enhancement of Anti-Tumor Potency / Antibacterial: Black garlic processed from ordinary white garlic clove in temperature- and humidity-controlled conditions showed enhanced anti-tumor potency. The aged black garlic yielded an increased amount of amino acids and organo-sulfur substance, S-allyl-L.cysteine (SAC), which might have contributed to the anti-tumor potency. Tumor cure rate was 50% against Meth A fibrosarcoma of BALB/c mouse. (44)
• Antifibrinolytic: The fibrinolytic system dissolves fibrin clots in circulation. Study showed the garlic extract exhibited fibrinolytic effect. Minimum concentration and maximum time showed the best results. (45)
• Antihyperglycemic / Antihypercholesterolemic / Combination with Ginger: Study evaluated the single and combined effect of Allium sativum and Zingiber officinale (ginger) against hyperglycemia and hypercholesterolemia in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Results showed the combined use of garlic and ginger is more effective in controlling hyperglycemia and hypercholesterolemia compared to either one alone. (46)
• Hypocholesterolemia: Study evaluated the effect of garlic supplementation on reducing cholesterol levels on 50 healthy patients given 3 g of raw garlic daily for a period of 90 days. Results showed a significant decrease in cholesterol levels: 13% (p<0.001) from 269.30 to 233.93 mg/dL in male patients and 10% (p<0.001) from 260.30 to 233.90 mg/dL in female patients. (47)
• H. pylori Inhibition: Study investigated the antibacterial effect of aqueous extract of garlic against Helicobacter pylori. The concentration of AGE (aqueous garlic extract) required to inhibit bacterial growth was between 2-5 mg/ml. Boiling and heat treatment reduced the efficacy of the AGE. An antibacterial synergistic effect was seen in combination with a proton-pump inhibitor (omeprazole) in rate of 250:1. (48)
• Effect on Pituitary-Gonadal Axis in Heat-Stressed Mice: Study evaluated the effects of garlic extract on reproductive hormones in female mice under heat stress. Results showed significant increase in estrogen and progesterone levels and suggests potential to neutralize negative effects of stress affecting the pituitary-gonadal axis and ovarian hormonal secretion. (49)
• Benefit
in Type 2 DM Patients / Powder and Aqueous Extract of Bulbs: Study showed both dry powdered plant and aqueous extract of bulbs of Allium sativum decrease blood and urine glucose levels in type 2 diabetic patients, especially in the group taking oral hypoglycemics with inadequate blood glucose control. (50)
• Effect of Supplementation on Biomarkers and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis / Clinical Trial: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study evaluated the effects of garlic supplementation on serum levels of some inflammatory biomarkers, clinical symptoms, and fatigue in women with active rheumatoid arthritis. After intervention, serum levels of CRP and TNF-α were significantly decreased. Pain intensity, tender joint count, disease activity score and fatigue were significantly decreased. Swollen joint count was decreased. No significant changes were observed for ESR. The improvement in inflammatory mediators and clinical symptoms suggest potential use of garlic as adjunct therapy in patients with RA. (51)
• Antifungal / Aspergillus sp in Otomycosis: Otomycosis is due to saprophytic fungi in a small percentage of otitis externa. Study evaluated the efficacy of garlic extracts against fungi of the genus Aspergillus. Aqueous garlic extract (AGE) and concentrated garlic oil (CGO) were used in the in vitro study. AGE and especially CGO showed antifungal activity with similar or better inhibitory effects than pharmaceutical preparations. (52)
• Ajoene / Antimicrobial, Antithrombotic, Cytotoxic: Ajoene, an organosulfur garlic compound, was extracted and evaluated for antithrombotic, antimicrobial, and cytotoxic effects. Ajoene showed the ability to dose-dependently inhibit microbial growth. Antithrombotic activity was visually confirmed by reduction in the size of the blood clot. Cytotoxicity testing showed non toxicity to VERO cells. (53)
• Co-Administration of Garlic and Black Seed (Nigella sativa) in Dyslipidemia / Clinical Trial: A prospective, randomized, double-blind trial evaluated the therapeutic effect of combination of blackseed with garlic for treatment of dyslipidemia. Results showed the combination was effective in correction of dyslipidemia and suggests large scale clinical trials to compare different doses. (56)
• Effect on Male Fertility: Systematic review studies the effects of garlic on male fertility in accordance with the PRISMA statement for systematic reviews and meta-analysis. A total of 18 experimental studies were included; 13 evaluated garlic and 5 compared garlic effect with various chemicals. All studies were conducted in invivo condition. Results indicated the potential effect of garlic on enhancing fertility and spermatogenesis, increasing the level of testosterone and improving testicular structure. Garlic can increase fertility probably due to its antioxidant properties. (57)
• Effect of Combined Herbal Formulation on Female Rat Fertility: Study evaluated the efficacy of Allium sativum, Curcuma mangga, and Acorus calamus extract combination on female rat fertility. All treatment compositions affected reproductive hormone and uterine histology profile. The composition of 36% A. sativum, 36% C. mangga, 28% A. calamus produced the highest estrogen and progesterone levels. Results suggest the combination therapy could be used to increase fertility in female rat. (58)
• Effect on Biofilm Formation / Antimicrobial: Study evaluated the antimicrobial activity of Allium sativum extract against biofilms of six pathogenic bacteria and their free-living forms using disc diffusion method. Results showed the extract discs did not have any zone of inhibition for the tested bacteria. However, the MICs of 0.078-25 mg/ml confirmed the high ability of the extracts for inhibition of planktonic bacteria. The extracts were efficient to inhibit biofilm structures in a concentration directly related to the inhibitory effect. Results suggest the extracts can be applied as antimicrobial agents against the pathogens, particularly in biofilm forms. (59)
• Suppression of Cytokine Production in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Study evaluated the possible therapeutic effects of garlic in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), whole blood and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Via inhibition of Th1 while upregulating IL-10 production, garlic extract treatment may help resolve inflammation associated with IBD. An invivo animal model determine the significance of these findings. (60)
• Toxicity and Repellency / Tribolium castaneum: Study evaluated the repellent activity and fumigant toxicity of garlic extract against larvae and adults of red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. The extract exhibited mortality that increased with increasing concentration and time. Results showed lethal and repellent effects of the extracts on T. castaneum. (61)
• Non-Toxic Corrosion Inhibitory: Study evaluated the inhibition efficiency of an aqueous extract of garlic in controlling corrosion of carbon steel in well water in the absence and presence of Zn by mass loss method. The formulation of 2 ml garlic extract and 25 ppm Zn offered 70% inhibition efficiency to carbon steel immersed in well water. FTIR spectra showed the protective film consists of Fe2+-allicin complex and Zn(OH)2. (62)
• Antibacterial Against Human Dental Plaque Microbiota: In-vitro study the antibacterial effect of different concentrations (5, 10, 20, and 100%)
of garlic extract against human dental plaque microbiota viz. Streptococcus mutans, S. sanguis, S. salivarus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Lactobacillus spp. Results showed all bacterial strains were inhibited by all test materials. Since all concentrations had similar effects further studies were suggested for the 5% extract. (63)
• Alleviation of Tebuconazole-Induced Liver Oxidative Stress: Study -evaluated the protective effect of Allium sativum oil against tebuconazole (TEB)-induced oxidative stress in the liver of adult rats. Results showed significant changes in some hematological parameters, along with changes in total cholesterol level and activities of hepatic enzymes ALS, , LDH, ALP) and 7-glutamyl transpeptidase. The co-administration of of ASO improved the status of all studied parameters, The protective effects against TEB-iduced liver injury was attributed to phenolic compounds. ( 64)
• Protective in Lead-Induced Hepatic and Testicular Damage / Combined A. sativum and Zingiber officinale: Study -evaluated the protective effects of combined aqueous extracts pf Allium sativum and Z. officinale against lead acetate-induced hepatic and testicular damage. Results showed a synergistic effect of A. sativum and Z. officinale in ameliorating the lead acetate induced hepatic and testicular damage as well as reduction in blood lead level in the rats. The synergisms may add to the reservoir of pharmaceutical and chemical templates for the exploration of new drugs. (65)
• Potent Anti-Bacillus anthracis Activity: Anthrax, a disease caused by Bacillus anthracis, remains an important but relatively neglected endemic disease of animals and humans in remote areas of the Indian subcontinent. Study evaluated commonly available edible plants used in traditional medicine for anti-Bacillus anthracis activity in a form amenable to use in endemic areas. Garlic (Allium sativum) was identified as the most promising candidate with bactericidal activity against Bacillus anthracis, consistently inhibiting its growth in agar-well diffusion assay and decreased viable colony forming units. GC-MS analysis of bioactive fractions showed the presence of phthalic acid derivatives, acid esters, phenyl group containing compounds, steroids, etc. The AGE displayed acceptable thermostability (>80%) anti-B. anthracis activity without antagonizing the activity of FDA-approved antibiotics used for anthrax control. Authors suggested further exploration of possible applications/use of aqueous garlic extract (AGE) in preventing anthrax incidences in endemic areas. (67)
• Antimicrobial Against Periodontal Pathogens: Study evaluated the efficacy of Psidium guajava and Allium sativum on periodontal pathogens Porphyromonas gingivalis and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Results showed both plants displayed significant antibacterial effect. The aqueous garlic extract (AGE) showed greater bacteriostatic activity against P. gingivalis with MIC of 16.6 µK/mL. (68)
• Inhibitory Activity Against S. pyogenes and P. aeruginosa: Study evaluated the antibacterial effect of Allium sativum against Streptococcus pyogenes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Results showed antibacterial activity with the extract showing greater effect on P. aeruginosa. (69)
• Natural Remedy for Metabolic Syndrome: The major features of Metabolic Syndrome includes central obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, low HDL cholesterol, hyperglycemia and hypertension. Study investigated the effect of garlic extract on the risk factors in metabolic syndrome patients along with conventional treatment. Results showed significantly improved glycemic control and HbA1c in the study group, along with improved lipid profile. Garlic can be used as adjunct therapy with diet and medicines in the management of metabolic syndrome. (70)
• Effect of Pre- and Post-Harvest Conditions on Chemical Composition and Bioactive Compounds: Garlic is considered one of the twenty most important vegetables throughout the world, either raw for culinary purposes or as ingredient in traditional and modern medicine. It has been proposed as one of the richest sources of total phenolic compounds among usually consumed vegetables. The review examines all aspects related to chemical composition and quality. The quality of garlic, expressed by chemical composition and bioactive compounds content, is highly dependent of both pre- and post-harvest conditions. Chemical compounds studied include (E)-ajoene, (Z)-ajoene, allicin, alliin, allixin, y-glutamyl-S-2-kpropenyl cysteine, diallyl disulfide, methyl allyl disulfide, methyl allyl disulfide, S=allyl cysteine, and 1,2-vinyldiithin. Maximum quality is affected by cultivation practices, genotype selection, growing conditions, the processing chain. and genetic variability among different garlic population and germplasm content of bioactive compounds. (71)
• Inhibitory Activity on Multi-Drug Resistant Streptococcus mutans: Study evaluated the in vitro inhibitory activity of garlic extract on MDR strains of Streptococcus mutans isolated from human carious teeth. All isolates, MDR and non-MDR S. mutans were sensitive to garlic extract with MIC ranging from 4 to 32 mg/ml. Study data suggest that mouthwashes or toothpaste containing optimum concentration of garlic extract could be used for prevention of dental caries. (72)
• Potential against Tooth Decay: Tooth decay is an irreversible progressive microbial disease caused by acid production due to bacterial carbohydrate fermentation on the teeth. The acid results in hard dental tissue degradation. Streptococcus mutans and S. sobrinus are the main pathogens of tooth decay. Kshirsagar evaluated the antibacterial activity of hard- and soft-neck garlic on S. mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus using well-diffusion method. Maximum inhibition zone of 24 mm was seen with hard-neck garlic, 18 mm with soft neck, and 17 mm with chlorhexidine. Study by Bin et al, Dewi et al, and Hoglund et al revealed different garlic extracts are effective against S. mutans and other cariogenic bacteria. As counterpoint, study by Ravi et al on methanolic extract of garlic bulbs against S. mutans did not show any antibacterial effect. The differences in result may be due to extraction methods, concentrations used, and research methods. (75)
• Blood Pressure Control Via Signaling Pathways / Review: Review focuses on the mechanical pathways of the blood pressure-reducing effects of garlic and its influence on several metabolic pathways. First, nitric oxide (NO) activation can lead to vasodilation. Garlic consumption can also promote vasodilation by suppressing the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and formation of prostaglandins, suppressing angiotensin-converting enzyme activity. Garlic-related vasodilation is related to its high sulfur-containing content associated with forming hydrogen sulfides (kATP),leading to hyperpolarization, which induces vasodilation. (76)
• Efficacy of Garlic Powder in Hemodialysis Patients: Interventional double-blinded randomized crossover study evaluated the effects of oral administration of Allium sativum powder on lipid profile, inflammation, and cardiovascular markers among 70 hemodialysis patients. In a clinical trial in 2019, Zare et al. showed 400 mg of standardized garlic extract twice daily for 8 weeks resulted in significant reduction in IL-6, CRP, and ESR. In this study, likewise, significant changes in ESR and CRP were seen in the garlic arm. Results showed Allium sativum powder demonstrated efficacy in lipid profile improvement and renal protective effects among hemodialysis patients. The small size of investigational samples may be insufficient to indicate effects of garlic on various biomarkers. More extensive trials with larger sample sizes are recommended to assess safety and efficacy. (78)
• Effect on Burn Wound Healing: Study evaluated the effect of topical cream from aqueous extract of garlic (0.8%, 0.4%, and 0.2%) on burn wound healing on a rat model. Burn wound contraction was increased in all groups of rats, with highest % of burn wound contraction at day 21 seen in rats treated with 0.4% garlic topical cream. The 0.4% topical cream treatment also showed more rapid granulation, formation of scar and healing on macroscopic exam, and higher amounts of tissue granulation with dense collagen deposition on microscopic exam after 21 days. Burn wound healing was not dose dependent. The 4% garlic cream was effective in improving burn wound healing of rats. (79)
• Antioxidant Effect in Healthy Postmenopausal Women: Study evaluated the antioxidant effects of garlic extract and crude black seeds consumption on blood oxidant/antioxidant levels in healthy postmenopausal women. Two garlic soft gels (equivalent to 1000 mg of fresh garlic bulb) and crude black seeds grounded to powder dose of 3 g/day were taken for 8 weeks. Results showed significant low levels of plasma malondialdehyde with increased erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase activities. Results suggest a beneficial effect on improved balance between blood oxidants and antioxidants in healthy postmenopausal women. (80)
Precautions
• Anticoagulant Use: Reports have suggested that garlic
may decrease platelet aggregation and have antifibrinolytic activity; therefore, should be used with caution in patients on anticoagulant
therapy.
• Induction of Cytochrome P450-34A: Concern for patients on cyclosporine and protease inhibitors. May
increase the effects of hypoglycemic drugs.
• Adverse Effects and Drug Interactions: While "garlic breath" and body odor are the most common and documented complains associated with garlic intake, case reports highlights various adverse reactions viz. allergic reactions like contract dermatitis, generalized urticaria, angioedema, pemphigus, anaphylaxis and photoallergy; alteration of platelet function and coagulation with risk of bleeding; burns with freshly applied garlic on the skin, especially with occlusive dressings. Garlic consumption by nursing mothers may cause some changes in the infant's behavior. Garlic may enhance the effects of anticoagulants like warfarin, fluindione and reduce the efficacy of anti-AIDS drugs like saquinavir. (also see: 34, 38 above) (55)
Availability
Wildcrafted.
Ubiquitous market produce.
Commercial: Tablets, extracts, capsules, powder and teas.




 • The anthelmintic property is due to allyl disulphide content.
• The anthelmintic property is due to allyl disulphide content. Uses
Uses

