 Botany Botany
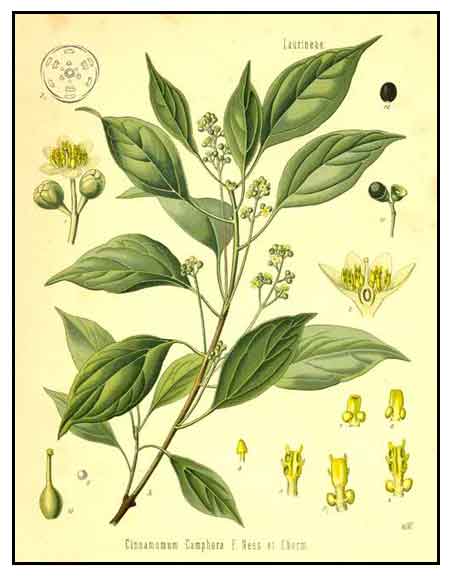
Camphor is a large evergreen tree growing to a height of 20 to 30 meters. Bark is pale, very rough, and fissured vertically. Leaves are green and glossy, with a waxy appearance, emitting the smell of camphor when crushed. In season, it produces a bright green foliage with masses of small white flowers. Fruits are berry-like, about 1 centimeter in diameter.
 Distribution Distribution
- Grows in subtropical countries, especially in East Asia.
- Native to Taiwan, southern Japan, southeast China and Indo-China.
Constituents
- Yields a colorless crystalline translucent mass.
- Camphor is obtained by passing steam through the chipped wood. The distillate contains camphor, which is separated and re-sublimed, yielding the essential oil of camphor.
- Roots, trunk, leaves, branches and fruits yield volatile oils.
- Hon-Sho leaf oil from C. camphora (Brazil) yielded 31 components, 94% of its composition made of monoterpenes and 2% by sesquiterpenes.
Oxygenated terpenes represented 81% of the total, camphor being the main component (68%) and linalool (9%). (11)
- GC and GC-MS analysis of essential oil of leaves yielded main components of
D-camphor (40.54%), linalool (22.92%), cineole (11.26%), and 3,711-trimethyl-3-hydrox-6,10-dodecadien-1-yl acetate (4.50%). (see study below) (13)
- Study of C. camphora isolated ten compounds identified as 4-hydroxysesamin (1), 3,3 ́-dihydroxy-4,4 ́-dimethoxytetrahydrofuran lignanoid (2), 3, 4- methylenedioxyphenyl-3 ́,9-dihydroxy-4 ́-methoxy- tetrahydrofuran lignanoid (3), lyoniresinol (4) , (+)-3 -(3, 4 – methylenedioxyphenyl)- 1,2- propanediol (5), isolariciresinol (6), taiwanin C (7), chinensinaphthol l(8), borneol (9) and daucosterol(10). (see study below) (15)
Properties
- Considered aphrodisiac, contraceptive, aborttifacient, antiseptic, lactation suppressing.
- Also considered uterotrophic, antitussive, anticonvulsant, anti-implantation.
Parts used
Gum, chopped wood.
Uses
Culinary
- Centuries of use as a culinary spice.
- In ancient and medieval Middle East and Europe, used as an ingredient for sweets.
- In China, used as confections flavoring during the Tang dynasty.
- In India, still used in cooking, especially dessert dishes.
 Folkloric Folkloric
- Used for colds, chills, diarrhea associated with colds, inflammatory affections, fevers, and hysterical complaints.
- Beneficial for gout, rheumatic pains, neuralgia, and irritations of the sexual organs.
- Externally, applied to inflammed affections, bruises, sprains, etc.
- In Iranian folk medicine, used as both aphrodisiac and anti-aphrodisiac: In small doses, aphrodisiac in exciting the reproductive organs, causing urethral heat and nocturnal emissions; in large doses, antiaphrodisiac in diminishing urino-genital irritation, and possibly decreasing libido and sexual performance.
Others
- Timber: In Japan, Taiwan, China and Indo-China, cultivated for camphor and its timber.
- Used as an important ingredient in the production of smokeless gunpowder, disinfectants, and celluloid. It has a wide range of medicinal uses. Safrole, produced from the residual oil after camphor extraction, is used in soap and perfume manufacture. (A large proportion of the world's camphor is now produced synthetically from pinene, a turpentine derivative, or from coal tar.) (16)
- Rituals: Burned in Hindu poojas and ceremonies.
Studies
• Anti-Inflammatory / Chemotype Diffrerences: Study of C. camphora showed an anti-inflammatory effect on the rat arthritis induced by Freund's adjuvant. The different chemotypes showed different pharmacologic activity and mechanisms of action. Results suggest that the difference be considered in clinical applications. (4)
• Essential Oils / Antimicrobial: Study investigated the inhibitory effects of CC on various inflammatory phenomenon. Results showed the anti-inflammatory actions of CC may be due to its modulation of cytokine, NO, and PGE2 production and oxidative stress.
• Sperm Motility Effects: Study indicate camphor has an effect on motility and viability of the human sperm and suggests a potential for the use of camphor as a local contraceptive. (6)
• Antimicrobial: Study of methanolic extracts of four plants, including C. camphora, showed potent antibacterial activity against six bacteria (E coli, Citrobacter, Shigella flexneri, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa and Yersinia aldovae) and significant to moderate antifungal activity against six fungal strains. (7)
• Effects on Sexual Behaviors: Study on the effects of camphor on sexual behavior in male rats showed sexual desire and sexual performance enhancing properties. (8)
• Review on a Traditional Medicine: Review focuses on the use of camphor as a remedy for daily minor problems, together with its new applications in the use for treatment of life threatening diseases such as cancer and diabetes. (10)
• Anti-Depressant / Oil: Study evaluated the antidepressant activity of CC oil using 3 doses (250, 500, and 750 mg/kg) in 2 in vivo models. Animals treated with 3 doses of CCO showed decrease in their immobility times in Forced Swim Test (FST) and Tail Suspension Test (TST). (12)
• Insecticidal / EO of Leaves:The essential oil of leaves of C. camphora and its active compounds showed potential to be developed as natural fumigants and insecticides for control of L. serricorne. Contact toxicity for L. serricorne adults showed an LC50/LD50 of 2.5 mg/L air and 21.25 µg/adult, respectively. (see constituents above) (13)
• Linalool / Anti-Molluscicidal and Larvicidal / O. hupensis and Schistosoma japonicum: Study evaluated the molluscicidal and larvicidal effects of linalool against O. hupensis and Schistosoma japonicum. Study identified 44 components from the leaf extracts of C. camphora. Linalool, the most abundant component, exhibited striking molluscicidal and larvicidal effects with LC50 of 0.25 mg/L for O. hupensis and LC50 of 0.07 mg/L for cercaria of S. japonicum. Linalool caused damage to gills and hepatopancreas of the snails, and disruption of cercarial integument. (14)
• Lignaloid / Inhibition on ß-Glucuronidase Release: Study yielded 10 compounds. Compound 1, 3,3 ́-dihydroxy-4,4 ́-dimethoxytetrahydrofuran lignanoid, showed inhibitory activity on the release of ß-glucuronidase from rat PMNs induced by PAF. (see constituents above) (15)
• Effect on Male Reproductive Traits: Study evaluated the effect of camphor on sexual behavior in male rams. Results showed caphor reduced semen volume, mass activity, testes length and live sperm percentage. (17)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Botany
Botany Distribution
Distribution Folkloric
Folkloric