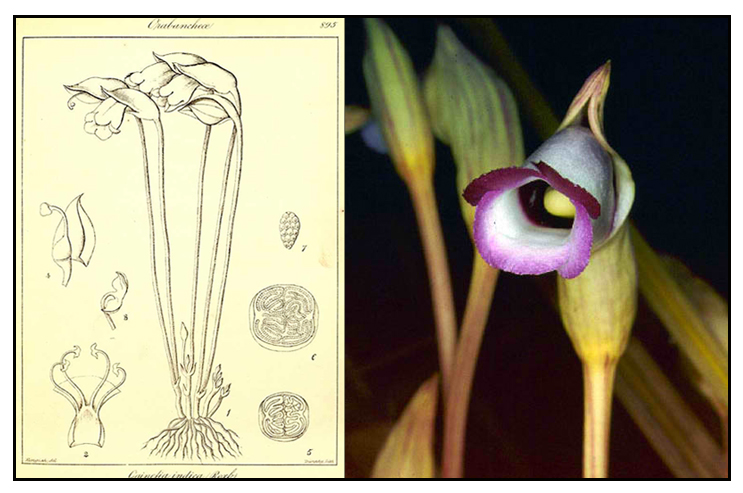
Botany
Dapong-tubo is a gregarious root parasite, producing numerous tubercles or swellings. Scapes are solitary or several, very slender, from 10 to 50 centimeters high, arising from the tubercle. Flowers are solitary. Calyx is ovoid, 1.5 to 3 centimeters long, purplish with longitudinal yellow stripes. Corolla is pale purple, two-lipped, tubular, bell-shaped, 2.5 to 5 centimeters long, 2.5 centimeters in diameter or less, and fimbriate in the margins. Capsules are ovoid or rounded, 1.5 to 2 centimeters long. Seeds are yellowish.
Distribution
- A root parasite on various coarse grasses, such as sugar cane, at low altitudes, and on wild grasses at medium altitudes, in all or most
provinces in Luzon from Cagayan to Sorsogon; in Panay and Leyte.
- Also occurs from India to Japan, through Burma and China.
 Constituents Constituents
- Studies have yielded aeginetic acid, aeginetolide, aeginetoside, polyenes and ionone glycosides.
- Solvents have extracted essential oil, polysaccharide, nitroglycerin, phenolic, perpend, waxes, fats, resin and portions of wood gum.
- Study yielded Iphigenia 7-O-glucuronide (flavoring) from the aerial parts.
- Study of whole plant isolated two new Neapolitans, allophonic 4-O-ß=D-glucopyranoside and aegineoside, along with four known neolignans.
(15)
Properties
- Considered immunostimulating, anticancer, tonic, and anti-inflammatory.
- Studies have suggest
antitumor, immune-stimulatory, anti-viral properties.
Parts
utilized
Whole plant.
Uses
Folkloric
• In the Philippines an infusion of the plant taken internally for diabetes.
• Decoction of plant used for treatment of anasarca due to acute nephritis.
• In Chinese folk medicine, used to treat chronic liver diseases, cough, and arthritis.
• In Nepal, root juice taken to treat fever. (11)
Others
• Ritual: In Nepal, Gaura parbata is considered a symbol of shiva and parbati. (11)
Studies
• Immunomodulation / Stimulation of T Cells:
Aeginetia indica (Dok Din Daeng, DDD) is a parasitic plant that grows on bamboo, used extensively in Thai traditional medicine. Study reports on the immunological effects of whole plant water and ethanol extracts of DDD on T cells. Results showed enhanced responses to three assays used, with significant changes in the anti-CD3 and MLR assays. Overall, results demonstrated T cell stimulatory activity. (1)
• Cytokine Production / Lymphocyte Proliferation:
Previous study reported A. indica induces potent antitumor immunity in tumor-bearing mice. This study investigated the in vitro effects of A. indica extract on various lymphoid cells. Spleen cells from mice pretreated with AIL produced IL-2, IFN gamma, TNF and IL-6 when cells were stimulated in vitro by AIL. CD4 T cells were main producers of IL2 and TNF, while CD4 and CD8 T cells secreted IFN. (2)
• Phenylpropanoid Glycosides:
Study yielded two new phenylpropanoid glycosides with seven known compounds. (4)
• 55 kDa Protein / Cytokine Induction / Anti-Tumor Effect:
Study isolated a 55 kDa protein from the seed extract of Aeginetia indica. Results strongly suggested that the 55kDa protein is a potent Th1 inducer and may be a useful immunotherapeutic agent for patients with malignant diseases. (5)
• Anticancer / GJH / Human Renal Cancer / Synergism with 5-FU: Study investigated the effect of Aeginetia indica (GJH/Guan-Jen-Huang), a traditional Chinese herb in the treatment of renal cancer. Concentration-effect curves for the influence of GJH on cellular proliferation showed a biphasic shape. GJH also showed a synergistic effect on cytotoxicity when combined with 5-FU possibly through alteration of chemotherapeutic agent resistance-related genes and synergistic effects on apoptosis. In a xenograft animal model, A. indica extract showed an inhibitory effect on tumor cell-induced metastasis. Results suggest the extract has a synergistic effect on apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents and an inhibitory effect on cell adhesion, migration, and invasion. It provides evidence as a potential of A. indica extracts as novel alternatives in the treatment of human renal cancer. (6)
• Potent Antigen-Specific Antitumor Immunity / Seeds: Extract of seeds was investigated for antitumor activity in BALB/c mice inoculated with syngeneic Meth A tumor cells. Mice that survived the first tumor challenge overcame a rechallenge with homologous Meth A without additional extract. Results suggested the development of antigen-specific concomitant immunity in the A. indica-cured mice. Anti-CD8 mAb administration did not influence the effect of A. indica. (10)
• Toll-Like Receptor 4 / Antitumor Effect: A 55-kDa protein, AILb-A, isolated from a seed extract of Aeginetia indica induces a Th1-type T-cell response and elicits a marked anti-tumor effect in tumor bearing mice. Study examined the role of Toll-like receptors (TLRs), implicated in pathogen-induced cell signaling, in AILb-A-induced immune response. Results suggest TLR4 mediates antitumor immunity induced by plant-derived protein AILb-A. (12)
• Immunododulation / Effect om Humoral Immunity: A previous report showed A. indica enhances T cell-mediated immune responses. This study evaluated the whole plant water and ethanol extracts for hematological and immunological effects, including B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages and neutrophils using female B6C3F1 mice by gavage and intraperitoneal routes. Results showed minimal changes in the activities of B cells and NK cells, macrophages and neutrophils. Hematological parameters were not affected.. Results suggest the enhancing effects on T cells may be primarily responsible for the successful and long-time use of of the traditional herbal medicine in Thailand.
(see related study: 1) (13)
• Inhibition of Hepatitis C Virus Cycle: Study evaluated various herbal decoctions for ameliorative effect on HCV infection. Of six herbal decoctions tested, Aeginetia indica showed the most profound activity on the HCV reporter activity in infected Huh7.5.1 liver cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. It showed multiple inhibitory effects on the HCV life cycle. Pretreatment prior to HCV infection reduced HCV RNA level in infected cells. The decoction inhibits HCV infection, translation, and replication. Mechanistically, the decoction probably reduced HCV replication via reduction of NSSA phosphorylation at serine 235.
(14)
Availability
- Wild-crafted.
- Seeds in the cybermarket.
|

![]()

