|
 Botany: Botany:
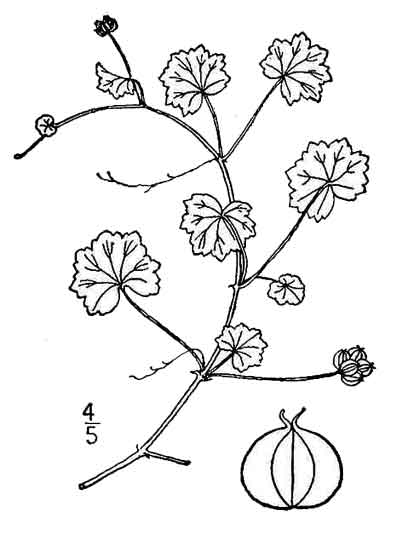
Kanapa is a delicate, creeping, nearly smooth herb with
the stems rooting at the nodes. Leaves are orbicular or subreniform, thin, about 1 centimeter in
diameter with heart-shaped base and margins somewhat lobed, the
lobes being short and having 2 or 3 teeth. Umbels are very small, with few flowers. Flowers are small, white, sessile, axillary, sepals lacking,
petals and stamens 5. Fruits are few, sometimes only 2 or 3 on a peduncle and
less than 1 millimeter long, ellipsoid, usually with red colored spots.
 Distribution Distribution
- Along small streams in shaded
ravines, ascending to 1,600 meters, in Cagayan, Ilocos Norte, Abra, Bontoc, Benguet, Laguna, Bataan, Quezon, Pangasinan, and Rizal Provinces in Luzon, and occasional in Manila in damp
shaded gardens at sea level.
- Occurs in India to Japan, Malaya, and the Mascarene Islands.
Parts
utilized
· Entire plant.
· Gathered throughout the year.
· Rinse after collection, sun-dry before use or use in
fresh state.
Constituents
- Roots contain vellarin and vitamin C.
- Study of methanolic extract of whole plants yielded seven new oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins, hydrocotylosides
I-VII and one known saponin, udosaponin B. (94
- Study yielded ten compounds: stigmasterol, daucosterol, hibalactone, genistein, daidzein,methyl-3, 4-dihydroxybenzoate, protocatechuic acid, caffeic acid, isorhamnetin, quercetin, hyperin. (See below) (9)
- Study yielded 28 compounds, seven isolated for the first time: chlorogenic acid methyl ester, 5-hydroxymaltol, (-)-angelicoidenol 2-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, n-butyl-β-D- fructopyranoside, apigenin, kaempferol, 4,2′,4′-trihydroxychalcone, and oleanolic acid. (10)
- Study of H. sibthorpioides for antioxidant phenolic compounds
yielded catechin, epicatechin, quercetin, and chlorogenic acid. (see study below) (23)
- Silica gel column chromatography isolated four
compounds identified as stigmasterol (1), daucosterol (2), genistein (3) and daidzein (4). (25)
- GC-MS study identified ten compounds: stigmasterol (1), daucosterol (2), hibalactone (3), genistein (4), daidzein (5), methyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzoate (6), protocatechuic acid (7), caffeic acid (8), isorhamnetin (9), quercetin (10), (see study below) (26)
Properties
- Sweet tasting, slightly minty.
- Juice is emetic.
- Considered depurative, febrifuge, expectorant, antitussive; antifebrile,
diuretic.
- Studies have suggested antioxidant, antiproliferative, immunomodulatory, hepatoprotective properties.
 Uses Uses
Edibility / Culinary
• Leaves are edible.
• Whole plant can be used as a potherb with its parsley-like aroma.
• Juice of shoots boiled and used as curry.
Folkloric
- Plant juice used for fevers.
- Poultice used for wounds and boils.
- Decoction of plant used for abscesses, colds, coughs, hepatitis, influenza,
pruritus, sore throat.
- Used for headaches and urinary problems.
- In Malaya, mixed with
sugar and cassia bark and given to children for coughs.
- Juice considered emetic.
- Leaves pounded with alum for poulticing scrotal skin ailments.
- In Nepal, plant used as diuretic and febrifuge; used for treatment of asthma.
- In China, used for hepatoma.
Also, an ingredient in Chinese herbal concoctions used for muscular
dystrophy. Also, used in treatment of hepatitis, fever, detoxification, psoriasis and edema.
- In the Arunachal Pradesh district of India, juice of the plant mixed with honey, used for typhoid fever. In the district of India, fresh plants are crushed and the juice extracted and three tablespoons are taken twice daily for five days. (7)
- In India, Juice of shoots eaten in dysentery. (19) Whole plant parts used as anthelmintic. (22) In Assam, India, leaves and roots used as digestive; and for rheumatism and menstrual problems.(28) In Assam, used as antipyretic; juice of plant in honey prescribed for typhoid fever.(29) In Assam, root juice of plant with Musa sapientum used in treatment of piles. (30)
Studies
• Antitumor / Immunomodulatory:
Ethanolic extract of HS showed anti-tumor activity with significantly
enhanced activity on murine hepatic carcinoma, sarcoma 180 cancer,
and uterine cervical carcinoma clones. Activity was comparable to that
of antitumor agent 5-fluorouracil. The extract also mediate immunomodulatory
effects as shown by promotion of thymus and spleen indices and humoral
immunity in mice. (2)
• Antioxidant / Antiproliferative:
H sibthorpioides was one of four Hydrocotyle species studied.
The results demonstrated that the phytochemicals might have a significant
effect on antioxidant and anticancer activities related to the amount
of polyphenols and flavonoids. The four species present a potential
source of natural antioxidants. Of the four hydrocotyle specie, HS and H batrachium had the lowest antiproliferative activity and H nepalensis, the highest activity. (3)
• Triterpenoid Saponins:
Study of methanolic extract yielded seven new oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins, hydrocotylosides I-VII and one known saponin, udosaponin B. (4)
• Anti-Heptic / HBsAg Inhibition:
Study yielded 10 compounds, viz., stigmasterol, daucosterol, hibalactone, genistein, daidzein,methyl-3, 4-dihydroxybenzoate, protocatechuic acid, caffeic acid,isorhamnetin, quercetin, hyperin. The herb showed no toxicity of Hep G2 2.2.15 cell, and its water extract exhibited inhibition to HBsAg at 1 mg/ml concentration with an inhibition ration of 27%. (9)
• Genistein / Hepatoprotective / Alcohol Induced Injury and Fibrosis:
Study evaluated the effect of genistein isolated from H. sibthorpioides on chronic alcohol-induced hepatic injury and fibrosis. Genistein exerted a preventative effect to ameliorate developing liver injury and even liver fibrosis induced by chronic alcohol administration in rats. (12)
• Asiaticoside / Age-Related Cognitive Benefits:
Study evaluated the effect of asiaticoside from Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides on the promotion of cognition in senescence-accelerated mice. Results showed treatment with asiaticoside from HS significantly improved learning and memory abilities in behavioral tests. Results suggest AHS may prevent spatial learning and memory decline by scavenging free radicals, up-regulating the activity of antioxidant enzymes, decreasing Aß, ameliorating dysfunction in synaptic plasticity and reversing abnormal changes in Ach and AchE activity. (14)
• Effect on In-Vitro Dengue Replication:
Study investigated the potential effect of Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides extracts against in vitro dengue viral replication using cell viability assay. Results showed H sibthorpioides had variable effects on dengue viral replication, depending on treatment, cell lines, and solvent types. (16)
• Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Compound / Asiaticoside: Study isolated a saponin, asiaticoside. It was shown to effectively suppress the levels of HBsAg/HBeAg, extracellular HBV DNA and intracellular DNA in a dose dependent manner. Asiaticoside could inhibit HBV replication both in vivo and in vitro. (17)
• Genistein / Hepatoprotective on Lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine Induce Hepatic Failure: Study showed genistein treatment significantly protected against LPS/D-GaIN-induced acute hepatic failure as evidenced by enzyme parameters and attenuation of histopathological changes. The protective effect was mainly due to its ability to block NF-kB signaling pathway for anti-inflammation response, attenuate hepatocellular apoptosis and increase HO levels. (18)
• Hepatoprotective / Thioacetamide Induced Injury: Study investigated the possible protective effects of genistein, a phytoestrogen, on liver injury in rats induced by thioacetamide. Results conclude that GEN attenuates liver induced injury in rats with TAA. The hepatoprotective effect is attributed to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. (20)
• Acute Oral Toxicity Testing: Study evaluated the acute oral toxicity of various extracts of H. sibthorpioides in Wistar albino rats per OECD guidelines. LD50 of all extracts were greater than 2000 mg/kbw. There were no significant change in body weight, behavior, renal functions, liver functions, and lipid profile. Hematologically, there was an increase in RBC count, hemoglobin production after administration of methanolic and aqueous extracts. (21)
• Antihyperlipidemic / Antioxidant / Phenolic Profile: Study evaluated the phenolic profile and antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant activities of G. sibthorpioides, Centella asiatica and Amaranthus viridis in experimental animal models. The polyphenol extracted from H. sibthorpioides showed excellent antioxidant activity with DPPH radical scavenging activity IC50 of 19.7 µg/mL and nitric oxide radical scavenging activity IC50 39.33 µg/mL. The extracted polyphenol also remarkably lowered the level of total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL-C, SGOT, SGPT, and MDA, while elevating HDL-C, SOD, and GSJ in high fat diet fed rats. (23)
• Phytoremediation / Cadmium / Invention: Invention reports on extraction of cadmium and other heavy metals in polluted soil. The method can be used for plant remediation of cadmium=related composite soil polluted by multiple heavy metals in mine district land, and farm soil with cadmium exceeding standards caused by irrigation with polluted water containing heavy metals. (24)
• Antihepatic Constituents / HBsAg Inhibition: GC-MS study of aetherolea from herbs of Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides identified fourteen of 48 compounds. Study showed no toxicity to HepG2 2.2.15 cell. Water extracts showed inhibition of HBsAg at concentration of 1 mg/ml, with inhibition ratio of 27%. (see constituents above) (26)
• Silver Nanoparticles / Antibacterial: Study evaluated the efficacy of various concentration of nano silver solution on three bacterial isolates: K. pneumonia, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus. Study demonstrated a simple, efficient, and ecofriendly synthesis of stable silver nanoparticles using an ethyl acetate extract of H sibthorpioides showing fairly superior antimicrobial activity against the tested human pathogens. (27)
Availability
- Wild-crafted.
- Dried whole plant in the cybermarket.
|


![]()

