|
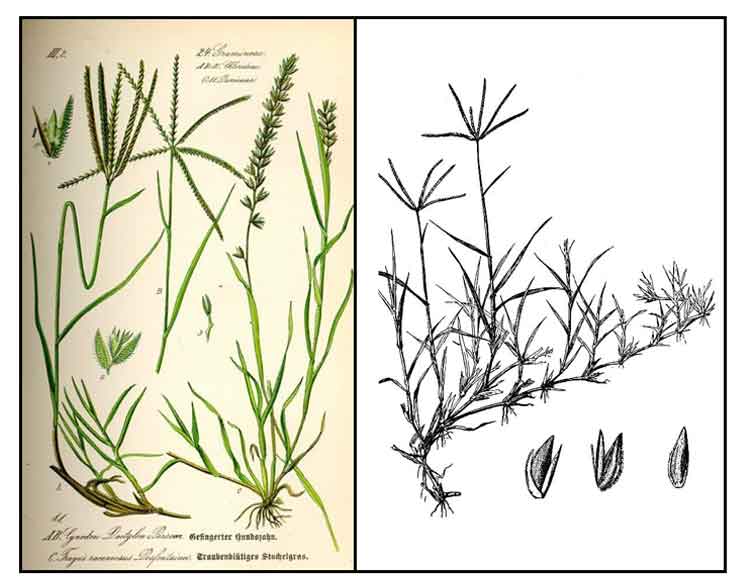 Botany Botany
Kawad-kawaran is a tropical and subtropical creeping
grass with slender, branched, prostrate, usually widely creeping stems, rooting at the
nodes and forming matted tufts, sending up erect, slender, flowering branches,
8 to 20 centimeters high. Leaves are 1.5 to 3 centimeters long. Spikes, numbering 3 to 4, are
2 to 5 centimeters long, narrowly linear, spreading, green to purplish.
Spikelets are imbricated, about 1.5 millimeters long.
 Distribution Distribution
- Commonly found throughout the Philippines,
in open grasslands, rice paddies, waste places, at low and medium
altitudes.
-
Bermuda grass is extensively used in urban and suburban
lawns. In the rural areas, collected for supplementary feed for
horses and carabaos.
Constituents
- Contains starch and cynodin, a substance
similar to asparagin.
- Plant yields crude proteins, mineral constituents, oxides of magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, sodium, and potassium.
- Whole plant yields sitosterol and carotene, vitamin C, cartone, palmitic acid, triterpenoids, alkaloids, ergonovine, and ergonovinine.
- Phytochemical screening of aqueous extract yielded flavonoids and glycosides. (see study below) (17)
- Methanolic extract yielded flavanoids, phenolic compounds, tannins, and phytosterols. (see study below)
(46)
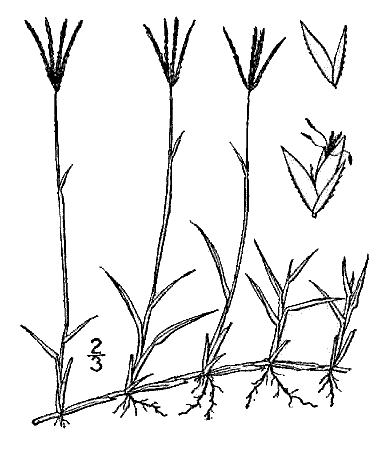 Properties Properties
- Diuretic, pectoral, demulcent, astringent, hemostatic, laxative, styptic.
- In Ayurveda, pungent,
bitter, fragrant, heating anthelmintic, antipyretic.
- According to Unani, bitter, laxative, tonic, aphrodisiac, emetic, emmenagogue,
expectorant.
- Studies have shown antidiabetic, hypolipidemic, antimicrobial,
diuretic, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, antiproliferative, chemopreventive, antiulcer, phytoremediative, immunomodulatory, wound healing, anti-emetic, bronchodilatory, antidiarrheal, neuroprotective properties.
Parts used
Entire plant.
Uses
Folkloric
• Decoction of the entire plant
used as diuretic.
• In India, crushed
leaves used as styptic in minor wounds to stop bleeding. Also used for inflammatory conditions.
• Decoction of root used as diuretic in dropsy. and syphilis.
- In Sind, the roots are used as a substitute for sarsaparilla.
• Infusion of root to stop bleeding from piles.
• Juice of plant applied to fresh cuts and wounds.
• Paste of plant applied to forehead in headaches.
• Used internally for epilepsy, hysteria, bleeding in dysentery, hemorrhoids, hematuria, menorrhagia, syphilis, prostatitis.
• Used for toothaches.
• Mixed with clove (Syzygium aromaticum) used as anthelmintic.
• Folk remedy for cancer, epilepsy, cough, dysentery, warts, snakebites.
• In Morocco, used in treatment of kidney stones.
Others
- Landscape:Bermuda grass is extensively used
in urban and suburban lawns.
- Feed: In the rural areas, collected for supplementary feed for horses and
carabaos. Reported to be highly nutritional for cattle.
- Homeopathy: Used for wound healing.
Studies
• Antidiabetic / Hypolipidemic: (1) Study of ethanolic extract of defatted C dactylon on Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats showed high antidiabetic potential and a good hypolipidemic profile, with a lowering of blood glucose, reduction of total cholesterol, LDL and triglycerides and an increase in HDL. (2) Study of aqueous extract of CD showed high antidiabetic potential along with significant hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects.
• Antimicrobial: Screening of Antimicrobial Activity of Cynodon dactylon and
Caesalpinia bonducella extracts: Results showed Cynodon extracts
are efficient against Pseudomonas species. (4)
• Chondroprotective / Anti-Inflammatory: Study showed a chondroprotective effect. The anti-inflammatory effect
may be due to stabilization of the lysosomal membrane. (5)
• Diuretic: Study on aqueous extract on the root stalk of Cynodon dactylon showed diuretic activity, with increased excretion of sodium, potassium, and chloride ions. Results were comparable to furosemide. (3)
• Cardioprotective / Inotropic: Study showed C dactylon exerted strong protective effect on right heart failure, partly through a positive inotropic action and improvement of cardiac functions.
• Chemopreventive / Antiproliferative: In a study of experimentally induced colon carcinogenesis in rats, C dactylon showed to be antiproliferative and antioxidative and induced apoptotic cell death. Treatment with the methanolic extract increased levels of antioxidant enzymes and reduced the number of dysplastic crypts. (6)
• Anti-Ulcer: Study evaluated an alcoholic extract of C. dactylon for antiulcer activity against pylorus ligated and indomethacin induced gastric ulcer models in albino rats. Phytochemical screening yielded flavonoids and proteins. The alcoholic extract showed significant (p<0.001) anti-ulcer activity, comparable to ranitidine, an effect attributed to the presence of flavonoids. (7)
• Curative/ Protective Effect on STZ-Induced Hepatic Injury: Study to evaluate the role of ethanolic extract of C. dactylon against hepatic complications in STZ-induced diabetic models showed a significant reduction of SGOT, SGPT, alkaline phosphatase, creatinine and urine sugar. A high LD50 validates a high margin of safety. (8) Study confirmed the protective effect on liver tissue in STZ-induced liver damage in Wistar rats as evidenced by significant (p<0.001) reduction of serum transaminases and ALP, together with demonstrable histopathological changes. (41)
• Immunomodulatory: In a study of mice immunized with sheep RBC, CD protein fraction enhanced the humoral antibody response to the antigen and significantly potentiated cellular immunity. (10)
• Cardioprotective: Study evaluated the cardioprotective effects of the plant against cardiac arrhythmias. Results showed the protective effects of Can. Dad against arrhythmias in isolated rat heart. Steroidal saponins were confirmed on phytochemical screening. It may act like digoxin, and anti inflammatory and direct mechanisms may also be involved. (11)
• Photorespiration: Study showed C. dactylon to possess phytohormones potential against defensible contaminated soil, fly ash, and aged petroleum sludge. It serves as a potential candidate for revegetation in heavy metal contaminated wastelands.
• Antimicrobial: Study evaluated seven different solvents of Cynodon dactylon for antimicrobial activity against some pathogens (Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Streptococcus pneumonia). Results showed an ethanol and ethyl acetate extracts showed broad spectrum activity to all tested pathogens. (14)
• Antidiabetic / Reduction of Hyperlipidemia / Leaves: Study of extract of leaves of C. dactylon showed reduction of hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia risk and also reduction of oxidative stress in diabetic rats. (15)
• Aphrodisiac and Male Fertility Effects: Study showed treatment of rats under stress with methanolic extract of C. dactylon showed a promising effect in overcoming stress-induced sexual dysfunction, sexual performance, fructose content of seminal vesicles, epididymal sperm concentration. Results showed the methanol extract to have aphrodisiac and male fertility effects. (16)
• Anti-Inflammatory: Study evaluated the anti-inflammatory activity of an aqueous extract of Cynodon dactylon using carrageenan, serotonin, histamine, and dextran induced rat paw edema and cotton pellet method. Results showed anti-inflammatory activity in all models studied. Activity was attributed to the presence of flavonoids. (17)
• Wound Healing Potential: Study evaluated the wound healing potential of gel preparations of aqueous and alcoholic extracts of C. dactylon on excision and incision wound healing models in albino wistar rats. Results showed significant wound healing potential with increased rate of healing in both models. (18)
• Anticonvulsant: Study of an ethanolic extract of C. dactylon showed anticonvulsant effect against MES (maximal electroshock) and PTZ (pentylenetetrazol) induced convulsions in mice, suggesting possible central nervous system depressant action. (19)
• Gastroprotective / Anti-Ulcer: Study evaluated the gastroprotective effect of extracts of CD in male albino wistar rats. Results showed significant reduction of ulcer index in extract treated rats of pylorus ligation, aspirin induced and ethanol induced gastric ulcer models. (20)
• Antioxidant / Ehrlich's Lymphoma Ascites: Study evaluated the level of enzymic and non enzymic antioxidants in Ehrlich's Lymphoma Ascites transplanted mice treated with EA fractions of C. dactylon. Results showed increased levels of enzymic and non enzymic antioxidants, suggesting lipid peroxidation inhibiting activity. (21)
• Antidiabetic / Leaves: Study evaluated various solvent extracts of leaves of C. dactylon in alloxan induced diabetic rats. A methanolic extract produced steep decline in blood glucose, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Other extracts also reduced elevated plasma cholesterol and urea levels in diabetic rats. (22)
• Anticancer Activity on Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma: Study evaluated the anticancer activity of C. dactylon in Swiss albino mice inoculated with EAC (Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma) cells. Treatment showed significant anticancer activities in the tested animal models, with enhancement of life span and restoration of hematological parameters. (23)
• Antiemetic Effect / Rhizome: Study evaluated a crude aqueous rhizome extract for anti-emetic activity in various emetogenic models. C. dactylon showed remarkable emesis suppressant activity when compared with standard drugs chlorpromazine, domperidone and metoclopramide. (24)
• Bronchodilatory Effect: A chloroform extract of Cynodom dactylon protected against acetylchloline (Ach) -induced bronchospasm in guinea pigs. The bronchodilator activity of CECD was attributed partly to the presence of scopoletin and mediated possibly through calcium channel blocking and phosphodiesterase inhibition. (25)
• Anti-Nephrolithiatic: Study evaluated the preventive effects of a hydroalcoholic extract of C dactylon roots on calcium oxalate calculi in rats. Results showed the extract was able to reduce the growth of urinary stones in rat. Urine oxalate level decreased in nephrolithiatic rats treated with the extract. (26)
• Hypotensive Effect / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated the effect of an aqueous extract of aerial parts of C. dactylon on mean arterial pressure in rats with fructose induced hypertension. Chronic administration of the aqueous extract of C. dactylon in hypertensive rats significantly reduced men arterial blood pressure. It also showed a significant decrease in pressor response to NA and adrenaline. The antihypertensive effect is possibly achieved by partly improving peripheral vascular resistance. (27)
• In-Vitro Anti-Cancer Activity / HEP-2, HeLa and MC Effect / Aerial Parts: Study supported the efficacy of Cynodon dactylon as an anticancer agent for HEP-2 laryngeal, HELA cervical and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines. Among the three cell lines CD showed more activity in HEP-2 laryngeal cell line. (28)
• Hepatoprotective / CCl4-Induced Toxicity / Leaves: Cynodon dactylon showed potent hepatoprotective activity attributed to its antioxidant property against CCl4 induced liver damage in mice. The effect was more significant than that of Silymarin. (29)
• Fluoride Bioadsorbent / Dactylon-Based Activated Carbon: Study evaluated the effect of application of Cynodon dactylon based thermally activated carbon for fluoride toxicity. Results showed C. dactylon bioadsorbent can be utilized to remove fluoride selectively from water. (30)
• Antidiarrheal: Study evaluated various extracts of Cynodon dactylon for antidiarrheal activity in castor oil induced diarrhea, gastrointestinal motility by charcoal meal and enteropooling models in albino rats. A methanol extract showed good antidiarrheal activity with significant decrease in gastrointestinal motility by charcoal meal and decreased weight on intestinal contents in enteropooling models. (31)
• Phytoremediation / Heavy Metal Pollution: Study showed Eisenia fetida, Cynodon dactylon and Vigna radiata can be used as effective indicators of soil health as they show positive accumulation results when exposed to heavily contaminated soils. (32)
• Anti-Inflammatory / Anti-Arthritic: Study evaluated the effect of C. dactylon against rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Orally administered C. dactylon produced significant attenuation in the inflammatory response, oxidative stress and ameliorated the arthritic changes to near normal condition. (33)
• Neuroprotective: Study evaluated the neuroprotective and antioxidant activities of an ethanol extract of C. dactylon against diazepam induced neurotoxicity in rat brain. Diazepam significantly increased levels of acetylcholinestrase, cholesterol, malondialdehyde (MDA) & superoxide dismutase (SOD) along with reduced level of glutathione-s-transferase (GST), glutathione (GSH) & glutathione peroxidase (GPx). The values are restored with administration of CD. Results suggest the ethanol extract may be a reliable adjuvant for neurotoxicity, with a potential as antioxidant and phytomedicine for neurodegenerative diseases. (34)
• Inotropic / Protective on Right Heart Failure: Study evaluated the effects of a hydroalcoholic extract of rhizomes of C. dactylon on cardiac contractility and cardiac functions in right heart failure in rats. Results showed a strong protective effect on RHF, in part by positive inotropic action and improvement of cardiac functions. (35)
• Antimicrobial / Anti-Pyretic: Ethanolic and methanolic extracts of C. dactylon showed good inhibitory effect for all tested bacterial and fungal strains. Extracts yielded flavonoids, alkaloids, phenols and glycosides. Both extracts also showed significant dose dependent antipyretic effect in yeast induced fever in experimental rats. (36)
• Antioxidant / Alpha-Amylase Inhibitory Activity: Selected isolates from ethyl acetate extract of Cynodon dactylon and Piper betle and the combination of both were found to have antioxidant activity alpha amylase inhibitory activity in different models. The selected isolates showed better activities in combined rather than individual form. (37)
• Angiogenic Effect: Study investigated the effects of an aqueous extract of C. dactylon rhizomes on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expressions in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs) and angiogenesis in carrageenan induced air-pouch model in rats. Results showed C. dactylon promotes angiogenesis probably through stimulating VEGF expression. (39)
• Anti-Parkinson's Effect / Rotenone-Induced Parkinson's Disease: Study investigated an aqueous extract of Cynodon dactylon for anti-parkinson's activity in rats induced by rotenone (2 mg/kg s.c.), Pretreatment with AECD resulted in significant (p<0.001) decrease in catalepsy and muscle rigidity along with a significant (p<0.001) increase in locomotion compared to the rotenone-treated control group. Results suggest a therapeutic potential of C. dactylon as antioxidant in Parkinson;s disease and other movement disorders. (40)
• Hypolipidemic Effect: Study reports on the study of efficacy of an Ayurvedic herbal formulation of C. dactylon on histopathological study and DNA fragmentation analysis in experimentally induced hypercholesterolemic rats. Histopathological study of thoracic aorta of C. dactylon treated group showed decreased atherogenicity compared to untreated high cholesterol diet fed rats. Results suggest the C. dactylon formulation was associated with hypolipidemic effects. (42)
• Anticancer / DEN Induced Hepatic Carcinoma / Roots: Study screened a methanolic extract of roots for hepatoprotective activity in diethyl nitrosamine (DEN) induced liver cancer in Swiss albino mice. Results showed significant anticancer properties. Enhanced levels of antioxidant enzyme and reduced amount of serum aminotransaminase may be major mechanisms in protecting the mice from hepatocarcinoma induced by DEN. (43)
• Dual Protection Against Epilepsy and Depression: Study of an ethanolic extract showed promising antidepressant as well as antiepileptic activity. The antiepileptic effect may be mediated through its GABA-mimetic action and the antidepressant effect may be mediated through 5HT2 antagonistic action. (44)
• Antifertility Activity: Study evaluated the effect of an aqueous extract of entire plant on reproductive organ weight and estrous cycle in female rats. Results suggest antifertiity activity with a significant (p<0.001) in the weight of uterus and significant decrease (P<0.001) in the weight of the ovaries of the treated group. Moreover, the estrous cycle was found to be irregular and disturbed. (45)
• Antitumor / Leaves: Study of methanolic extract of leaves of Cynodon dactylon against Ehrlich ascitic lymphoma (ELA) in Swiss albino mice showed significant antitumor activity and hepatoprotective effect. (see constituents above) (46)
• Phytoremediation Potential / Crude Oil Contaminated Soil: A greenhouse experiment investigated the phytoremediation potential of Cynodon dactylon in soils contaminated by various concentrations of crude oil. Study showed with increased contamination, there was positive correlation with residual total petroleum hydrocarbon content uptake in the plants. Results showed C. dactylon to be highly effective in the remediation of crude oil contaminated soils through bioaccumulation ability by roots and shoots. (47)
• Cardiac Effects / Negative Inotropic and Chronotropic Effects: Study evaluated a phenolic fraction of C. dactylon for cardioprotective activity using isolated frog's heart perfusion method. The fraction produced negative inotropic and chronotropic actions on isolated frog heart. The effect was inhibited by atropine indicating mediation through muscarinic receptors. (48)
• Silver Nanoparticles / Leaves: Study reports on a rapid, reliable and eco-friendly process for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cynodon dactylon leaf extract. (49)
• Cardioprotective Against I/R-Induced Arrhythmias: Study investigated the possible antiarrhythmic effects of C. dactylon against ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced arrhythmias in isolated rat heart. Results showed protective effects in isolated rat hearts probably by increase in myocardial contractility and as a result of hemodynamic factors. (50)
• Haemostatic Effect / Nanoparticles / Leaves: Study evaluated the haemostatic activity of Cynodon dactylon in albino rats through bleeding time (BT) and clotting time (CT) determinations. In the study, freshly prepared juice of C. dactylon significantly reduced both BT and CT. Effect on bleeding time may be through effect on integrity of blood vessel or enhancing the formation of platelet plug. Clotting time effects may be through enhancement of coagulation process via intrinsic pathway involving factors XII, XI, IX or VIII. (51)
• Antagonist to Angiotensin II Type I Receptor: Study in diabetes induced retinopathy rat models evaluated the ability of secondary metabolites of C. dactylon to serve as an antagonist to angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Activation of this receptor play a vital role in diabetic retinopathy. Study yielded 24 compounds as secondary metabolites of a hydroalcoholic extract. Sixteen ligands showed effective binding with the target protein; didodecyl phthalate, diazoprogesteron, and 9,12-octadecadienoyl chloride may be considered compounds capable of interacting with angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Results suggest the metabolites of C. dactylon could serve as a natural antagonist to AT1 that could be used to treat diabetic retinopathy. (52)
• Silver Nanoparticles / Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity: Silver nanoparticles were synthesized using C. dactylon leaf extract. The biologically synthesized AgNPs showed dose-dependent cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells and concentration dependent antimicrobial activity against E. coli, S. aureus, M. luteus, and S. typhimurium. (53)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|


![]()

