 Botany Botany
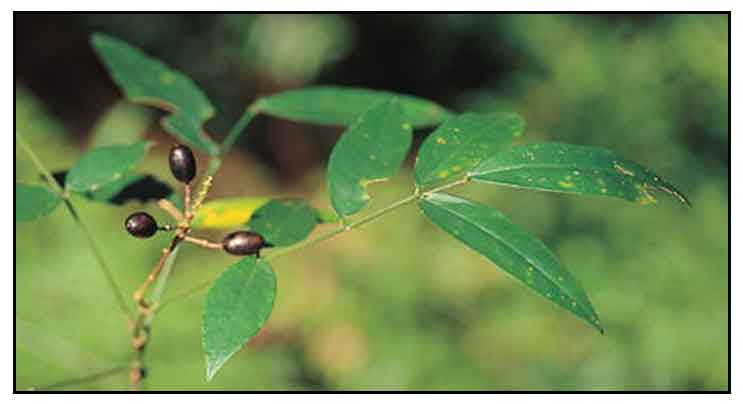
Laguan is an erect, tough, unarmed shrub about 0.5 to 1.5 meters high. Leaves are alternate, smooth, long-petioled, and odd-pinnate, with 3 to 5 leaflets which are oblong, 10 to 15 centimeters in length, often rounded at the base and pointed at the tip. Flowers are borne in considerable numbers in simple, peduncled, axillary racemes. Corolla is white, about 1.25 centimeters long or twice the length of the calyx. Pods are oblong, 1 to 2 centimeters long, and very turgid, purplish black when mature, and contain a single, large seed.
 Distribution Distribution
- Of local occurrence on the higher mountains from northern Luzon to Mindanao.
- Also occurs in India to the Riu Kiu Islands from Taiwan southward to Java.
Constituents
- Seeds contain cytisine.
- Study isolated two new prenylflavanones, euchrenones a7 and a8 from the roots and stems.
- Study yielded 40 chemical compounds. The highest, kaur-16-ene, was found in the root (51.29%) and stem (36.13%). Palmitic acid was 16.7% in roots, 34.79% in stems, 23.55% in leaves, 13.79% in skin of seed,
and 36.13% in seeds. Vitamin C was highest in the seed skin. (3)
- Roots yielded three new flavonoids, viz., 5,2',4'-trihydroxy-6-(3,3-dimethylallyl-6''',6'''-dimethylpyrano[2''',3''':7,8)] flavanone(euchrenone a9),5,4'-dihydroxy-6(3,3-dimethylallyl)-5'''-hydroxyisoproyldihydrofurano [2",3":7,8]isoflavone(euchrenone b10) and 2-methoxymaackiain, together with known compounds kushenol E, 6,8-di(3,3-dimethylallyl)genistein, osajin, warangalone, derrone 4'-O-methyl ether, alpinumisoflavone 4'-methyl ether and feruloyl hexadecayl ester. (4)
- GC-MS analysis of seed extract yielded 9 compounds, among which were eugenol 17%, terpenoid compounds (trans-caryophyllene 17.55% and a-humulene 1.67%),
and carboxylic acid group (hexadecanoic acid 1.30%, 9.12-hexadecadienoic acid 3.66%, hexanedioic acid 10.06%, and 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid 2.30%.), along with the alkaloid compound (matrine 8.45%). (see study below) (7)
Properties
- Seeds are bitter and poisonous.
- Considered tonic and aphrodisiac.
- Study has shown
hypolipidemic property.
Parts used
Roots, seeds.
Uses
Folkloric
- In the Philippines, roots are chewed as a cure for snake bites.
- Seeds are used for diseases of the chest.
- Although considered poisonous,
used as a tonic and aphrodisiac.
Studies
• Hypolipidemic / PPAR Activation: Study of EH fruit extracts showed significant PPARa activation, increased PPARa target gene expression and regulated protein expression for lipid metabolism. Results indicate that E. horsfieldii shows potential as a natural lipid-lowering agent. (1)
• Antidiabetic / Antioxidant / Leaves: Study showed E. horsfieldii leaf extract can prevent oxidative stress by decreasing the levels of MDA (malondialdehyde) and can improve the histopathological profile of pancreatic ß-cell damage in alloxan induced diabetic Wistar rats at 140 mg/kbw dose. (5)
• Antioxidant Capacity / Effect on SOD and GPx Activities: Study evaluated the effect of an ethyl acetate extract of E. horsfieldii leaves on increasing activity of SOD (superoxide dismutase) and GPx in blood plasma of Wistar rats with maximum physical activity. Results showed antioxidant capacity with IC50 of 393.95 mg/l on DPPH assay and total flavonoid level of 6619.72 mg QE/100g or 6.62% QE. (6)
• Antihyperglycemic / Repair of Damaged Pancreatic ß-Cells / Seeds: Study evaluated the effectiveness of seed extract in repairing ß-cell pancreatic damage in alloxan induced hyperglycemic Wistar rats. Results showed pranajiwa seed extract at 5mg/kbw reduced the rate of ß-cell destruction and structural changes of pancreatic ß-cell tissue histopathology in the Wistar rats. (see constituents above) (7)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Botany
Botany Distribution
Distribution