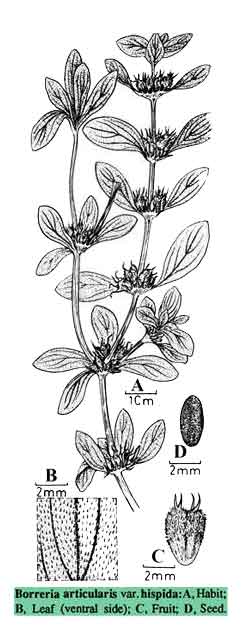
 Botany Botany
Landrina is a procumbent, branched, hairy or rough herb, 10 to 14 centimeters long. Branches are greenish or purplish, ascending, stout and 4-angled. Leaves are ovate, spatulate, or elliptic, 1 to 3.5 centimeters long, 0.8 to 1.7 centimeters wide, pointed or rounded at the tip. Flowers are 4 to 6, occurring in whorls in the axils of leaves. Calyx-teeth are linear-lanceolate. Corolla is pale blue or white, 5 to 10 millimeters in length. Fruit is a hairy capsule about 5 millimeters long. Seeds are oblong, granulate, opaque, unusually variable, 3 millimeters or less in length.
Distribution
- From the Batan Islands to Batangas and Laguna in Luzon, and in Mindoro, Panay and Basilan, in open, dry places at low and medium altitudes,
- Also occurs in India to China and Malaya.
 Constituents Constituents
- Methanolic extract yielded flavonoids and amino acids.
-
Various extracts of whole plant yielded alkaloids, carbohydrates and glycosides, phytosterols, fixed oil and fats, saponins, phenolic compounds and tannins, protein and amino acid, coumarins, and flavonoids.
- Preliminary phytochemical screening of hydroalcoholic extract of dried plant powder yielded alkaloids, carbohydrates glycosides, proteins, amino acids, phytosterols, triterpenoids, phenolic compounds and flavonoids, with absence of saponins, fixed oils, fats, gums, and mucilages. (see study below)
(7)
- Various extracts of seed oil yielded
saponins, tannins, phenolics, steroids, essential oil, flavonoids, and terpenoids, with an absence of alkaloids, glycosides and carbohydrates. Seed oil content was 43.60% in the petroleum ether extract and 19% in the methanol extract. (see study below) (14)
Properties
- Roots possess properties similar to sarsaparilla.
- Considered alterative, tonic, cooling, demulcent, aphrodisiac, constipative.
- Used as antieczemic, antibacterial, antidiarrheal, antidysentery.
- Studies have suggested antioxidant, antibacterial, cardioprotective, constipative, antihyperlipidemic, antinociceptive, free radical scavenging, anticancer, antidiabetic antituberculosis, hepatoprotective properties.
Parts used
Leaves, seeds.
Uses
Edibility
- In the Konkan, the plant is eaten with other herbs as vegetable.
Folkloric
- In the Philippines, leaves are brewed in decoction and used as astringent for hemorrhoids.
- In Martinique, plant is used as tonic and stimulant. Also used for hemorrhoids.
- Leaves applied to the head in cases of headache, with it cooling effect, somewhat allaying the pain.
- The seeds in confection are cooling and demulcent; used for dysentery and diarrhea.
- Seeds considered by some as aphrodisiac.
- Used as alternative therapy for diabetes.
- In Siddha medicine, seeds used to cure diarrhea; roots used as tonic.
- In Tamil Nadu, India, paste made from crushed seeds used to treat stomach problems. (22) In India, plant decoction used for headache and seeds used as stimulant and for treatment of internal injuries of the nerves and kidney. (23)
- Used for headaches, constipation, hypertension, scabies, IBS, erysipelas, mouth ulcers, abscesses, and as antifertility medicine.
- In Ayurveda, used as antioxidant, contraceptive, stomachic, emollient; vapor of plant inhaled to kill tooth worms. Leaf decoction used for piles, diarrhea, dysentery. Leaf paste applied to head for cooling effect. (23)
Studies
• Cardiac Benefits: Study showed BHE-treated rat hears showed improved post-ischemic ventricular function and reduced myocardial infarct size and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Results suggest BHE has a potential as a plant-based nutraceutical for the management of cardiovascular diseases. (1)
• Antibacterial: Study of extracts of Borreria hispida showed antibacterial activity against B subtilis, B pumilus, S aureus, P aeruginosa, E coli and K. pneumonia, with the methanolic extract found to be the most effective. Results supports its use as remedy for superficial bacterial and fungal infections in traditional medicine. (2)
• Antioxidant: In an vitro study, a methanolic extract of whole plant of Borreria hispida yielded a high amount of flavonoids, and suggests a potential source of natural antioxidant. (3)
• Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Activity / Seeds: K3, a 35 KDa protein, was purified from the seeds of Borreria hispida. The F3 protein exhibited cytotoxic activity, with dose-dependent antiproliferative and apoptotic activity against lung (A549) and cervical (HeLa) cancer cells. (6)
• Constipation Activity / Dried Plant Powder: Study evaluated constipating activity of Spermacoce hispida using albino Wistar rats, using the extract in an irritable bowel model in lieu of loperamide. A hydroalcoholic extract of whole plant showed significant constipation activities (p<0.05) compared to standard drug loperamide. (see constituents above) (7)
• Antihyperlipidemic Activity : Study evaluated the antihyperlipidemic effect of Spermacoce hispida seed-flavonoid rich fraction by a dose-dependent study. Results showed significant reduction of total cholesterol, triglycerides, plasma phospholipids, free fatty acids, LDL cholesterol, and VLDL-C, with significant elevation of HDL. Activity was attributed to the presence of ursolic acid, quercetin, isorhamnetic, and hesperetin. (8)
• Free Radical Scavenging Potential: Study evaluated in vitro free radical scavenging potential of various extracts of whole plant of Borreria hispida. The methanolic extract showed strong antioxidant activity by inhibiting DPPH and superoxide anion scavenging and iron chelating activities. It contained a noticeable amount of total phenols and can be used as an easily accessible source of natural antioxidants and as possible food supplement. (9)
• Antihyperlipidemic Activity / Seed: Study evaluated an ethanolic seed extract for antihyperlipidemic activity against triton-WR-1339 induced hyperlipidemia in rats. Results showed it effectively suppressed the triton induced hyperlipidemia, suggesting a potential protective role in coronary heart disease. (10)
• Anti-Nociceptive: Study evaluated an ethanolic extract for anti-nociceptive activity using an acetic acid-induced abdominal constrictions and Tail immersion models. Results showed significant analgesic potential compared to standard drug Aspirin and Pentazocine. (11) Study evaluated the analgesic activity of aqueous extract of S. hispida on thermal and chemical induced pain in adult albino mice. Results showed analgesic activity, with all test doses showing significant delayed reaction time in hot-plate method and reduced number of writhing in chemical method. (21)
• Anti-Cancer / Ovarian Cancer Cell Line / Antioxidant / Leaves: Study evaluated a leaf extract for antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. The extract dose dependently inhibited growth of cell lines in human ovarian cancer cell line PA 1, and also showed to be a rich source of antioxidants. (12)
• Hepatoprotective / Nitrobenzene Induced Hepatotoxicity: Study evaluated the hepatoprotective activity of an ethanolic extract of whole plant against nitrobenzene induced hepatic damage in rats. Histopathological analysis showed severe centrilobular necrosis, fatty infiltration and lymphocyte infiltration. Treatment resulted in decreased liver marker enzymes activity and lipid peroxidation levels with increase in antioxidant status. (13)
• Antimicrobial / Seed Oil: Study evaluated various extracts of seed oil for antimicrobial activity. Studies on Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms reveal the methanolic extract to show significant activity compared to petroleum ether extract. (14)
• Acute Toxcity Study / Seeds: Study evaluated the hydroalcoholic extract of seeds of Spermacoce hispida in albino wistar rats in single doses of 500, 1000, 2000 mg/kbw. No mortality or clinical signs of toxicity were observed. The LD50 and maximum tolerable dose was greater than 2000 mg/kbw. (17)
• Constipation Activity: Study evaluated the constipative activity of S. hispida using albino Wistar rats in the setting of irritable bowel syndrome using the extract in lieu of loperamide. (18)
• Hepatoprotective / Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Hepatotoxicity: Study of an ethanolic extract of Spermacoce hispida against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in rats showed significant protective effect from hepatic damage. (19)
• Cardioprotective / Mitochondrial Energy Production / Seeds: Study evaluated the effects of pretreatment with S. hispida on isoprenaline-induced myocardial infarction in heart mitochondrial function in experimental rats. Results showed a protective effect which can be attributed to the activation of mitochondrial energy metabolism. (20)
• Anti-Anxiety: Study evaluated the anxiolytic activity of ethanolic extract of Spermacoce hispida in Swiss albino mice using elevated plus maze test and bright and dark box test models. Results showed the ethanolic extract have anxiolytic activity better than diazepam. (24)
• Selenium Nanoparticles / Hepatoprotective Against Acetaminophen Toxicity: Study reports on the synthesis of selenium nanoparticles (Sh-SeNPs) glutathione using Spermacoce hispida conjugated with SAG (s-allyl glutathione). Pretreatment of the nanoparticles attenuated the APAP toxicity-induced elevation of kidney and liver injury markers in the blood circulation and protected the morphology of liver and kidney tissue. SAG-Sh-SeNPs exhibited enhanced protection compared to Sh-SeNPs due to synergistic effect, protecting the liver the kidney against APAP toxicity through reduction of oxidative stress, enhancement of endogenous antioxidants and protection of mitochondrial functions. (25)
• Comparison of Selenium and Silver Nanoparticles / Anti-Inflammatory / Anticancer / Antibacterial / Leaves: Selenium and silver nanoparticles were synthesized using S. hispidal aqueous leaf extract. Both Se and AgNPs showed concentration dependent antioxidant activity. SeNPs showed potent anti-inflammatory property, antibacterial, and anticancer activity against human cervical cancer cell compared to AgNOs. (26)
• Novel Nano Niosomes as Drug Delivery System / Antituberculosis Activity: Study evaluated the antituberculosis activity of S. hispida extracts and the development of a novel nano noisome based drug delivery system for the extract of SH to enhance antituberculosis activity. The developed niosomal nano-carrier system exhibited prolonged release of drug and enhanced the in vitro antituberculosis activity of Spermacoce hispida extract. (27)
• Effect of Flavonoid-Rich Fraction / Up-Regulation of PPAR-α mRNA / Seeds: Study evaluated the influence of a flavonoid-rich fraction from SH seed (S-Frf) on PPAR-α gene expression, plasma and erythrocyte antioxidants status, protein metabolism,, and marker enzymes in diabetic hyperlipidemic male albino Wistar rats. Results showed the S-Frf had an antihyperlipidemic effect, improved antioxidant status, and alleviated liver and kidney damage associated with HFD-fed-STZ rats by up-regulating PPAR-α mRNA. (28)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Botany
Botany Constituents
Constituents