|  Gen info Gen info
- Pityrogramma, the silverback ferns or goldback ferns, is a genus of fern in the subfamily Pteridoideae of the family Pteridaceae.
- Etymology: The genus name Pityrogramma derives from the Greek word pitura-gramma, referring to the lower surface of the fronds obscured by rod-like secretions. The species epithet calomelos is from the Greek word kalo-melanw, meaning "beautifully dark". (33)
 Botany Botany
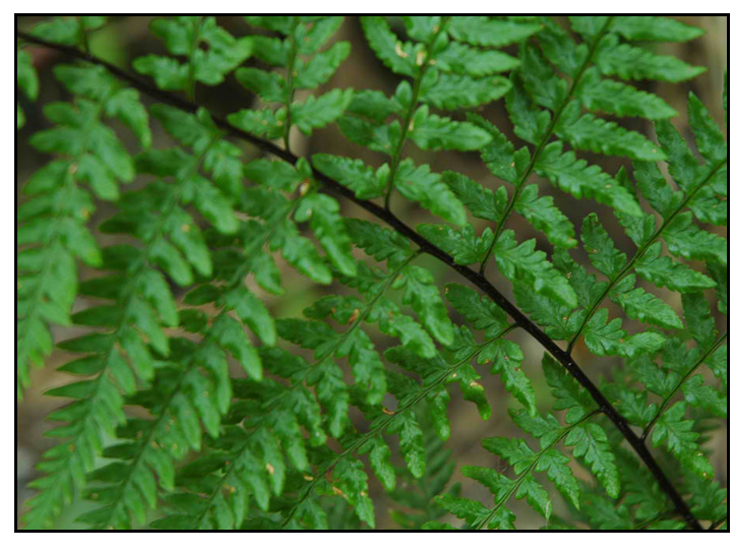
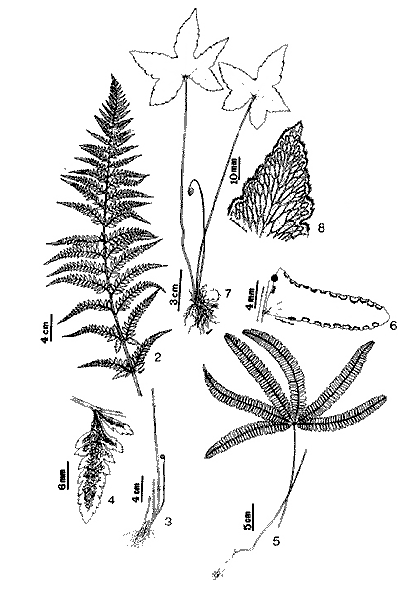
Pakong-gubat is a wild and exotic fern. Rhizomes are
stout, erect and oblique, with brown scales. Stipes are tufted, angular,
brown to black, polished, and 5 to 30 centimeters long. The fronds are 3-pinnatifid,
10 to 90 centimeters long and 5 to 30 centimeters wide, when well developed, and easily
recognized by their white or yellowish bottom surface. Pinnae are close
linear-lanceolate in shape, 2 to 5 centimeters wide. Sori are linear and forked,
at length occupying the entire lower surface of the lobes.
Distribution
- Introduced.
-
In the provinces of Nueva Ecija,
Bulacan, Rizal, Camarines Provinces and Manila in Luzon; and from Mindoro, Panay and Mindanao.
- Native range is Mexico to Tropical America.
 Constituents Constituents
- Farinose exudate of P. calomelanos isolated five new complex flavonoids named calomelanos F-J.
- Aerial parts yielded flavonoids compounds viz. 2',6'-dihydroxy-4'-methoxydihydrochalcone, kaempferol, and quercetin. (see study below) (11)
-
Quantitative determination of phytochemical showed a total phenol content of 2.58 mg/g GAE and flavonoids of 187.13 ± 20.88 mg/g quercitin and tannic acid of 65.35 ± 1.66 mg/g tannic acid.
- Qualitative screening of leaf extracts yielded alkaloids, phenols, tannins, flavonoids, reducing compounds, polyuronides, saponins, and terpenoids. (17)
- Study isolated a flavonoid compound, 2',5'-dihydroxy-4'-methoxydihydrochalcone, from the dichlor-methane extract of P. calomelanos.
(24)
- Phytochemical screening of rhizome and frond extracts revealed secondary metabolites such as alkaloids, cardioglycosides, phenolics, saponins, tannins, terpenoids, steroids, quinones, flavonoids, and glycosides. (see study below) (28)
Properties
- Considered astringent, analgesic, anti-hemorrhagic, pectoral, depurative, emmenagogue, antipyretic, antitussive.
- Studies have shown antibacterial, phytoremediation, trypanocidal, cytotoxic, mucolytic, anticancer, antibiotic potentiating, anti-epimastigote, anthelmintic, antifungal, fluconazole potentiating, immunostimulant properties.
Parts utilized
Whole plant, leaves, fronds.
 Uses Uses
Folkloric
- In Malaysia, leaves reportedly cooked and eaten. (27)
Folkloric
• Decoction of the plant with roots
of Cynodon dactylon and styles of Zea mays is used for kidney afflictions.
• Whole plant used for kidney troubles.
• In Trinidad and Tobago,
used for kidney and urinary problems.
(16)
• Plant infusion used to increase male sexual stamina and to treat menorrhagia. In Guyana, aqueous extract drunk or applied locally to treat venereal disease. (12)
• In Malaysia, whole plant used for kidney troubles; rhizome used for treatment of dysentery. (23)
• In Tamil Nadu, India, decoction of whole plant taken orally early in the morning to treat kidney problems, fever, cough, and colds. Rhizome is ground into a juice and taken orally to treat asthma. (25)
- In the Konkan region of Maharashtra, India, decoction of young fronds used for kidney trouble; juice of leaves and rachis used for gastric disorders and as anthelmintic. (26)
Others
• Ornamental: In New Guinea used as urban ornamental; tips of fronds used in head-dress.
(14)
• Ethnoveterinary: In India, leaf decoctions used to cure ox and cattle wounds on the neck. (26)
Studies
• Cytotoxicity Screening: Screening of 11 ferns for cytotoxic
and antitumor potential with special reference to Pityrogramma calomelanos. (1)
• Dihydrochalcone: its farina produces the cytotoxic and anticancer compound dihydrochalcone.
• Comparable Uptake Efficiency in Arsenic-Treated Soils and Water: Arsenic is a ubiquitous trace metalloid widely distributed in the environment, contributed to by metal smeltering, mine tailings, and arsenic pesticides. A comparative study of arsenic efficiency uptake by Pteris vittata and P. calomelanos in amended soils and tainted water showed P. calomelanos to perform better than P. vittata. (2)
• Remediation of Contaminated Rice Fields: The presence of high levels of arsenic (As) i rice is significant as it is an important world food staple. Even baby rice products are reported to contain levels of inorganic As exceeding safe standards. Ferns are able to "compete" against rice plants, reducing the amount of As that reaches the rice plants.
• Complex Flavonoids in the Farinose Exudate: Study yielded five new complex flavonoids from the farinose exudate of Pityrogramma calomelanos - calomelanos F-J. (3)
• Phytoremediation Potential / Arsenic-Contaminated Soil: A comparative study of arsenic hyperaccumulation at a historical As contaminated cattle dip site in Australia predicts P. calomelanos var. austroamerican will take approximately 100 years to reduce the total As to below 20 mg/kg-1 compared to ≥200 years for P vittata. (7)
• Antiepimastigote / Chagas Disease: Study investigated the antiepimastigoe activity of an ethanol and hexane fraction of P. calomelanos against T. cruzi (CL-B5 clone). Results showed tripanocidal activity and suggests a potential source of antiepimastigote natural product with only moderate toxicity toward healthy human cells. (8)
• Antimicrobial Enhancement: Study evaluated an ethanol extract and methanol fraction of P. calomelanos for antimicrobial and modulatory activities against various bacterial and fungal strains. Results showed good activity against S. aureus when associated with aminoglycosides and against species of Candida when associated with benzoilmetronidazol. Results showed direct and modulating activity, enhancing the antimicrobial activity of drugs and combating microbial resistance. (9)
• Antimicrobial: Study assessed the validity of Carribean plant species in its traditional use for treatment of bacterial infections against five bacterial strains viz. S saprophyticus, S. aureus, E. coli, H. influenza, P. aeruginosa and P. vulgaris, and fungus C. albicans. Study confirms the traditional use of P. calomelanos for the treatment of kidney infections. associated with stones. (10)
• Flavonoids / Cytotoxicity on Murine Leukemia Cells: Study of aerial parts of the fern yielded flavonoid compounds viz. 2',6'-dihydroxy-4'-methoxydihydrochalcone, kaempferol, and quercetin. All isolates showed cytotoxicity against murine leukemia P-388 cells. (11)
• Effect of Soil pH on Remediation of Arsenic Contaminated Soils: Study showed the remediation of As-contaminated mining soil by P. calomelanos can by improved by changing the soil pH from 4.6 to 6.8.
• Anthelmintic: Study evaluated the anthelmintic activity of various ferns in sheep infected with Haemonchus contortus. An ethanolic extract of Pityrogramma calomelanos has better efficacy (91%) than A. radiata (84%), D. cochleata (78%), D. quercifolia (65%) A. aureus (56%) and H. arifolia (49%). (13)
• Enhancement of Aminoglycoside Activity: Study evaluated ethyl acetate and hexane fractions of P. calomelanos showed good activity against Staphylococcus aureus when associated with gentamicin. The fractions showed no relevant activity against Candida species. (15)
• Anti-Leishmanial / Leaves: Leishmaniasis is caused by parasites of the genus Leishmania. Study evaluated ethanol extract and fractions of P. calomelanos for cytotoxicity and in vitro leishmanial activity against promastigote forms of Leishmania brasiliensis. Results indicated a leishmanicidal effect from the ethanol extract and ethyl acetate fraction. The hexane and methanol fractions showed no leishmanicidal activity nor cytotoxic effect. Phytochemical screening yielded alkaloids, a class of secondary metabolites with known leishmanicidal activity. (18)
• Potentiation of Fluconazole Activity and Inhibition or Candida Morphological Changes: Study investigated the antifungal activity of fern species Lygodium venustum and Pityrogramma calomelanos against Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis strains. The extracts only presented week antifungal activity. However, P. calomelanos potentiated the activity of fluconazole and both extracts inhibited the morphological changes in Candida species, indicating potential pharmacological activity as modulators of fungal biology. (19)
• Arsenic Phytoremediation: Pityrogramma calomelanos grown in a phytofiltration unit was able to reduce the water arsenic concentration from 40 ppb to below 10 ppb (IS Environmental Protection Agency standard). The ferns were effective in keeping the water arsenic concentration below 10 ppb over the entire experimental period of 1 week. The results suggest potential for a low-cost set-up where arsenic contaminated water is passed through plastic pipes planted with ferns can facilitate household purification of drinking water. (20)
• Chalcone / Cytotoxic / Antitumor Potential: Study evaluated aerial parts of 11 species for in cytotoxicity and antitumor potential. In vitro cytotoxicity of methanolic extracts showed that for all the species, except P. calomelanos, more than 40 mcg of extract/ml produced 50% cell death within 3 hours. The cytotoxic component in the farina of P. calomelanos fronds was isolated and identified as 2'6'-dihydroxy-4'4-dimethoxy dihydrochalcone. In mice injected with Ehrlich ascites cells, life span was increased by 52 and 57% when a liposome preparation of the chalcone at 5 and 25 mg/kg was administered, respectively. (21)
• Potentiation of Aminoglycoside Against Staph aureus: Study reports on the enhancement and additive effect of P. calomelanos on aminoglycoside against a multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus. Results suggest the ethanol extract and ethyl acetate fraction of P. calomelanos can be a source of plant derived products with antibiotic modifier activity, positively affecting the antibiotic activity of aminoglycosides. (22)
• Antibacterial / Rhizome and Fronds: Study evaluated the comparative analysis and antibacterial efficacy of rhizome and frond extracts of Pityrogramma calomelanos. Extracts were subjected to antibacterial assay using disc diffusion assay against four pathogenic strains such as Salmonella typhimurium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli and Xanthomonas campestris. Results showed ethyl acetate and methanolic extracts were more active than petroleum ether and aqueous extracts. Frond extracts exhibited significant antibacterial activity compared to rhizome extracts against all tested strains. (see constituents above) (28)
• Mucolytic Activity: Study evaluated the mucolytic activity of methanol extract of silver fern. In vitro mucolytic activity was assessed by decreasing the viscosity of intestinal mucus cow. Test showed the existence of flavonoid compound. Results showed mucolytic activity at concentration of 0.6% equivalent to acetylcysteine 0.1%. (29)
• Toxicity and Anticancer Potential: Study evaluated the molecular structure of phenolic compound isolated from the dichloromethane extract of silver fern's aerial part and toxicity activity test. The isolate was identified as 2',2'-dihydroxy-4'-methoxydihydrochalcone. It showed toxicity against Artemia salina in BSLT with LC50 of 3.957 µg/mL. The isolate as categorized as highly toxic and has potential as an anticancer agent. (30)
• Pesticidal Efficacy against Spodoptera litura / Phytoecdysteroid Fraction: Spodoptera litura, Tobacco armyworm, is a serious polyphagous lidopteran insect pest that infests about 115 plant species worldwide. Study evaluated a phytoecdysteroid fraction isolated from the fern and its effect on survival, growth, and developmental periods of Spodoptera litura. S. litura larvae treated with the fraction showed maximum larval mortality (68%) in 2000 ppm (LC50 of 1473 ppm). Pupation, pupal weight, and adult emergence were decreased with higher concentrations. Treatment with minimal concentration resulted in various developmental deformities, which may be due to interaction of the phytoecdysteroid fraction with the insect endocrine system. Results suggest the phytoecdysteroid mediated biopesticide formulation has potential as alternative to commercial chemical insecticides. (31)
• Immunostimulant / Flavonoid Kaempferol: A flavonoid compound, kaempferol, was separated from an acetone extract of silver fern. Based on carbon clearance, the isolated flavonoids showed immunostimulant activity with phagocytosis index of 1.846. (32)
Availability
- Wild-crafted.
- Ornamental cultivation.
|



 Botany
Botany
 Uses
Uses

