Gen info
Etymology: The genus name Eleusine derives from Eleusis, a Greek city where the goddess of grain Demeter, was worshiped. (The Roman equivalent is Ceres). The species epithet is from Latin, indicus, referring to India. (59)
Botany
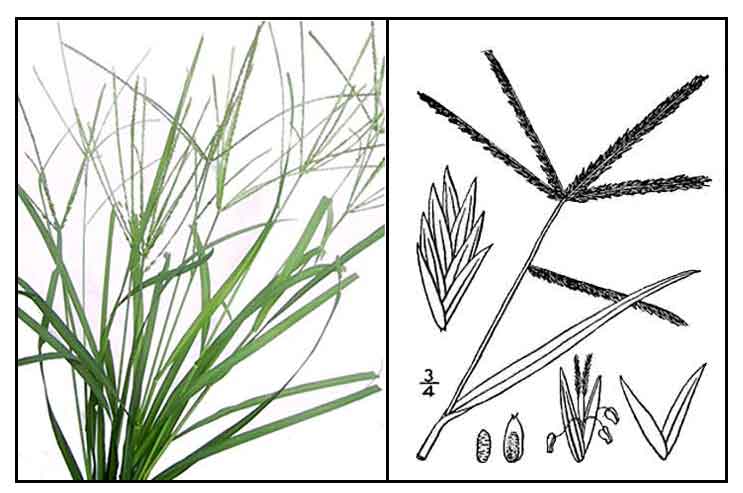
Paragis is an annual, erect, tufted,
adventitious, glabrous grass, 10 centimeters to 1 meter in height. Leaves are 10 to 30 centimeters long, sometimes involute when dry, 3 to 7
millimeters wide, distichous, rather flaccid, with flattened sheaths. Spikes are 3 to 6, all in a terminal whorl, or one or two lower down, 2.5 to 10 centimeters long, 3 to 5 millimeters thick. Spikelets are very numerous, crowded, 3- to 5-flowered, 3 to 4 millimeters long, the first glume 1-nerved and small, the second, 3-nerved, and the third and succeeding ones ovate, acute.
 Distribution Distribution
- Native to the Philippines.
-
An abundant weed in waste places and along river banks, roads, and settled areas throughout the Philippines.
- Strictly xerophytic.
- Also found throughout warm countries.
Constituents
- Ash of leaves contain SiO, 16-47%; CaO, 10-13%; and chlorine, 6-7%.
- Study showed the dry matter content to be 35.8%, crude protein 12.4%.
- Methanol extract yielded flavonoids +++, tannins +, alkaloids ++, cardiac glycosides ++, anthracene glycosides ++, anthraquinones +.
- Elemental analysis (dry weight basis expressed as ppm) yielded: calcium 21240 ± 213, potassium 25050 ± 223, magnesium 4049 ± 28, phosphorus 2375±84, B 24.74 ± 1.19, copper 55.12±2.14, iron 455.0 ± 5.10, manganese 163.8 ± 2.64, molybdenium 13.49 ± 1.32, and zinc 80.23 ± 2.17. Calorific value cal/g was 3753 ± 223, ash % 11 ± 0.22. (see study below) (21)
- Study of aqueous extract for total phenolic content yielded 14.9±0.002 mg/g gallic acid equivalent per gram of extract. (see study below) (11)
- Studies have isolated two main flavonoids i.e., schaftoside (6-C-β-glucopyranosyl- 8-C-α-arabinopyrano-sylapigenin) and vitexin (8- C-β- glucopyranosylapigenin). (39)
- In a study of 10 botanicals, E. indica yielded the highest calcium content (165.0 mg/100 g). Iron content was 9.7 mg/100 g. The plant also yielded alkaloids, carotenoids, flavonoids, saponins, and steroids. (45)
Properties
- Plant considered diuretic,
anthelmintic, diaphoretic, febrifuge.
- Studies have shown anti-inflammatory, antiplasmodial, antidiabetic, phytoremediative, pancreatic lipase inhibitory, antioxidant, antileishmanial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, anticonvulsant, antibacterial, nephroprotective properties.
Parts used
Whole plant, leaves, roots, leaf juice.
Uses
Edibility / Culinary
- Roots and seeds are edible.
-
Roots
eaten raw, young seedling raw or cooked.
- Grain is a famine food in India and parts of Africa.
- Used as millet, cooked whole or ground into flour and used in making cakes, gruel.
Folkloric
- Decoction of fresh leaves used as anthelmintic.
- Decoction of the fresh plant used as a diuretic and for dysentery.
- In Surigao del Sur, decoction of leaves drunk three time daily as diuretic. (41)
- In Sablan, Benguet Province, decoction of leaves used for kidney problems and arthritis. (45)
- The Mamanwa tribe of Mindanao drink decoction of whole plant
three times daily to relieve fatigue and flatulence. (53)
- Whole plant mixed with gogo used for dandruff; also prevents hair loss.
- Decoction or fresh juice of leaves prescribed after childbirth.
- Decoction of roots used for fever.
- Poultice of leaves applied to sprains and lumbago.
- Decoction of whole plant (roots to flowers) taken for hemoptysis.
- Used for hypertension.
- Bakwiri people of West tropical Africa use infusion of whole plant for hemoptysis.
- Ayta people of Porac, Pampanga burn dried leaves and stems as repellent against hematophagous insects. (24)
- In Singhalese Materia Medica, reported as useful for sprains and dislocation.
- In Malaysia, decoction of roots used for
asthma. Also used for hastening placenta delivery after childbirth, treatment of dysmenorrhea, asthma, fever, urinary infection, hemorrhoids.
- In coastal Guyana, decoction of plant used
to relieve pains from abdominal muscle strain; applied to wounds to
stop the bleeding. Decoction of grass used as tonic and to relieve bladder
disorders.
- In Malaya, leaf juice given after childbirth
to help expel the placenta.
- In Sumatra, used as anthelmintic.
- In Cambodia, used for fevers and liver
complaints.
- In Venezuela, seed decoction given to infants suffering from black jaundice.
- In Nigeria, leaves used for diabetes and malaria.
- In Colombia, decoction of plant for diarrhea, dysentery and convulsions.
- In Cameroonian folk medicine, used for diarrhea, dysentery, epilepsy, and intestinal occlusion. (18) Also used in the treatment of infertility in females. (24)
- In Sri Lanka, for muscle sprains, roots or the entire plant mixed with scraped coconut and a piece of Curcuma domestica is pounded well and heated till cooked, then packed over sprained muscles and bandaged.
- In Myanmar, leaves used for treatment of hypertension. (26)
- In Bangladesh, roots used in a mixture of herbal plants for the treatment of prolapsed uterus. (32) Crush plants are bandaged to areas of fractures. Plant decoction drunk to treat convulsion in children. Whole plant extract taken for liver disorders. (47)
- In India, roots used for treatment of snake bites: 20 g of roots are crushed into a paste with 10 g of Zingiber officinale and nine pieces of black pepper, half taken orally with honey and the other applied to the snake bite. (43)
Others
- Weaving: Stems used for making
mats, baskets, hats.
- Paper: Plant suitable for paper making.
- Ritual: In Bontoc, used in mangmang rituals. Malays hold the grain in their hand in
spirit-summoning rituals.
- Fodder: Grass, when young, is eaten by cattle.
- Veterinary: In West Bengal, India, used as antipyretic for herbivores. After collection, plants at succulent stage are washed and whole root and 1-2 centimeters of stems and fed fresh to ailing animals. (29)
Studies
•
Inhibition of Airway Inflammatory Processes: C-glycosylflavones from the aerial
parts of Eleusine indica inhibit LPS-induced mouse lung inflammation: Study may justify the
popular use of EI against airway inflammatory disorders. (3)
• Apoptotic Induction Activity: Study of grass extracts of D. aegyptium and Eleusine indica showed selective inhibitory growth inhibition effect on human lung cancer and cervical cancer (HeLa) cells. The activity was probably mediated through induction of apoptosis. (5)
• Antiplasmodial / Antidiabetic / Leaves: Study evaluated an ethanolic leaf extract of E. indica as antidiabetic and malarial remedy. Results showed significant (p<0.01-0.001) schizonticidal activity during early and established infections with significant mean survival time. Treatment of alloxan-induced diabetic rats a leaf extract caused significant reduction in fasting blood glucose levels in acute and prolonged treatment study. (6)
• Nutritional Potential / Fodder: Study showed the dry matter content to be 35.8%, crude protein 12.4%. Forage was found to be fairly palatable when fed to goats, with no adverse effect. E. indica presents a potential alternative for the problem of green roughage scarcity. (10)
• Hepatoprotective/ Antioxidant: Study evaluated an aqueous extract of E. indica against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatic injury in rats. Results showed hepatoprotective effects which may be attributable to its antioxidant and free radical scavenging property. The extract reduced the stable DPPH level in a dose-dependent manner. (see constituents above) (11) Study concluded E. indica and T. latifolia could be used as hepatoprotective agents with the potential for treatment or prevention of degenerative diseases where oxidative stress is implicated. (16)
• Antibacterial/ Antioxidant: Study evaluated various extracts of Eleusine indica for antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-cancer effects. A MeTH extract showed the highest total phenolic contents and scavenging activity on DPPH assay. An ethyl acetate extract showed broad spectrum antibacterial activity against all tested bacteria except B. subtilis, while a hexane extract showed remarkable activity against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and P. aeruginosa. Study failed to show cytotoxicity against tested cancer cell lines. (13)
• Fodder / Nutrition Analysis: Study showed a dry matter content of 35.8% and crude protein content of 12.4%. The forage was found fairly palatable with no adverse effects when fed to goats and suggests a potential source for green roughage during periods of scarcity. (14)
• EDTA-Assisted Heavy Metal Phytoremediation: Study showed the possibility of using the grass E. indica for phytoremediation especially phytostabilization of Cu, Cr and possible phytoextraction of Pb. (15)
• Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity / Obesity Treatment Potential: Study evaluated the lipase inhibitory activities of methanolic extracts of thirty two selected medicinal plants in Malaysia for potential use in the treatment of obesity. Eleusine indica showed the highest pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity of 31.36%, with no significant difference between its methanol extract and the standard drug Orlistat. (17)
• Antiplasmodial / Antidiabetic / Leaves: Study an ethanolic leaf extract of Eleusine indica for antiplasmodial activity in Plasmodium berghei infected mice and antidiabetic activity in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Results showed significant (p<0.01-0.001) schizonticidal activity during early and established infection, comparable to standard drug chloroquine. Leaf extract showed significant (p<0.01) reduction in FBS of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. (20)
• Mineral Analysis: In a study of 10 grasses for mineral analysis, Eragrostis amabilis and Eleusine indica showed large amounts of major and minor elements which suggest potential for cultivation to fulfill mineral deficiency in livestock feeding. (see constituents above) (21)
• Remediation of Crude Oil Polluted Soil: Study evaluated the potential of two weed plants (Eleusine indica and Panicum maximum) and a crop plant (Pennisetum glaucum) in remediation of crude oil contaminated soil. Of the three, P. glaucum showed greatest potential to remediate. E. indica had greatest impact on soil with 2%, 3%, and 4% levels of crude oil. (22)
• Antioxidant / Cytotoxic / Antileishmanial / Leaves: Study evaluated an ethanol leaf extract of Eleusine indica for cytotoxicity activity against HeLa cells, antioxidative burst activity, and antileishmanial activity. The extract showed moderate cytostatic activity, significantly inhibited oxidative burst activity and also exhibited moderate antileishmanial activity against promastigotes of Leishmania major inn vitro. (23)
• Anti-Herpes Simplex Virus Type-Activity: Study evaluated the antiviral activity of methanol extract of E. indica whole plant in relation to mode of action, attachment, penetration or virucidal activity. Results suggest E. indica is safe with an antiviral and prophylactic potential via inhibition of viral attachment, penetration, and virucidal effect. (25) MTT screening against Vero of crude extract showed the crude extract and hexane fraction showed non-cytotoxicity with CC50 values of 2.07 and 5.62 mg/ml, respectively. The antiviral activity towards HSV-1 for the ME and hexane fraction were 12.2 and 6.2, respectively. (27)
• Crude Oil Remediating Potential: Study compared the crude oil-remediating potential of Cynodon dactylon and Eleusine indica in a completely randomized experimental screen-house design. Results showed E. indica has a higher crude oil pollutant remediating potential on soil than C. dactylon. (28)
• Lipid-Lowering Effects on High-Fat-Diet Hyperlipidemic Rats: Study investigated the lipid-lowering effects of various extracts of E. indica using both in vitro and in vivo models. Hexane extract exhibited strong potential in the inhibition of porcine pancreatic lipase (27.01±5.68%). Acute oral toxicity on animal models was Category 5 (low hazard) on the Globally Harmonized System with no observed mortality, clinical toxicity symptoms, and pathologic changes. The HE also significantly reduced body weight, improved serum lipid profile, with reduction in TC, LDL, triglycerides and increase in HDL. (30)
• Antimicrobial / Antidiarrheal / Anthelmintic: Study evaluated the antimicrobial activity of E. indica on selected pathogens usually associated with diarrhea i.e., S. dysenteriae, E. coli, S. typhi, S. aureus, S. faecalis and L. lactis. Results showed concentration dependent antimicrobial activity with the aqueous extract showing highest susceptibility. Plant also showed marked anthelmintic activity against Strongyloides stercoralis. (31)
• Growth Inhibition and Pro-Apoptotic Action: Study evaluated the possible mutagenicity and/or cytotoxicity activity of E. indica using the Allium test to investigate root growth, mitotic index and micronuclei formation. Results strongly suggest the plant possess cytotoxic compounds with microtubule affinity interaction without mutagenicity activity. (33)
• Anticonvulsant: Study evaluated the anticonvulsant potential of ethanolic extract of Eleusine indica in albino Wistar mice. Results showed dose-dependent statistically significant (p<0.001) increase in latency of clonic convulsions and decrease in duration of tonic convulsions. The protection provided against mortality was similar to standard drug diazepam. (34)
• Antibacterial: Study evaluated the in-vitro antimicrobial potentials of whole plant extracts of E indica against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, B. subtilis and one fungi, C. albicans. The ethyl acetate extract showed the widest zone of inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus and also showed broad spectrum of antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa, E. coli and B. subtilis. None of the extracts showed activity against Candida albicans. Activity was attributed to the presence of flavonoids, alkaloids, and tannins in the extracts. (35)
• Diuretic / Toxicity Study: Study evaluated the diuretic potential and secondary metabolic profile of crude alcoholic extract and fractions of Eleusine indica. The crude alcoholic extract was non toxic at 1000 µg/mL on brine shrimp assay and 2,500 mg/kbw in mice. An aqueous ethanolic fraction was found to possess the highest diuretic activity, significantly higher than standard furosemide. (36)
• Lipid Lowering and Anti-Obesity Effects: Study evaluated the lipid-lowering effects of fractionated crude methanolic extracts of E. indica in both in-vitro and in-vivo models in Sprague-Dawley rats. A hexane fraction demonstrated marked inhibition in development of obesity and hyperlipidemia in HFD-induced hyperlipidemic rats. Study also demonstrated anti-obesity properties suggesting a potential role as an anti-obesity agent from natural sources. (37)
• Antiurolithiatic / Roots: Study evaluated the antiurolithiatic potential of different concentrations of Eleusine indica root extract on ethylene glycol induced nephrolithiasis in Rattus novergicus (albino rats). Results showed antiurolithiatic effect. The concentration of 500 mg/ml showed best results with reduction of serum creatinine, BUN, and uric acid, with prevention of nitrituria, proteinuria and oxaluria among the treatment groups. (38)
• Toxicological Assessment: Study evaluated the toxicological effects of E. indica extract in adult albino Wistar rats. Silymarin was used as standard drug. Extract was administered at doses of 200, 400, and 600 mg/kg on alternate days for 28 days. While organ weights were not affected, animal weights increased significantly (p<0.01-0.0010). At high doses, the spleen and lungs showed moderate inflammation. The lungs also showed moderate interstitial fibrosis. Study suggests its use as herbal remedy should be for short periods at a time. (39)
• Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition / Antihypertensive / Leaves: Study evaluated solvent fractions and decoction of E. indica leaves for ability to inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), an important component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system critical in the regulation of arterial blood pressure. An ethyl acetate fractions exhibited the highest antihypertensive action with 51.51% inhibition. (40)
• Ascaricidal /
Leaves and Stems:Study evaluated an alcohol extract from fresh leaves and stem of Eleusine indica and decoction of fresh samples against hog Ascaris lumbricoides. Of all solutions tested, the 20% water solution of alcohol free extract concentrate exhibited the highest ascaricidal effect. (42)
• Inhibition of 5-LOX and COX Enzyme Systems /
Aerial Shoot: Recent studies supported use of E. indica in inflammatory processes as evidenced by reduction of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Study evaluated the anti-inflammatory activity of E. indica in dual inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) / cyclooxygenase (COX). Preliminary screening of crude methanolic extract and fractions showed significant dual 5-LOX.COX inhibition. Results suggest E. indica elicits its anti-inflammatory activity by targeting arachidonic acid metabolic pathyways. (49)
• Safety Study on Heavy Metal Risks: Study evaluated the concentration of three heavy metals i.e., lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), and chromium (Cr) in paragis grass concoction from three towns along Laguna Bay. Samples were prepared with 20 g of paragis grass in 1L of water boiled for 15 min. For non-carcinogenic risks associated with consumption of the samples, estimated Target Hazard Quotient (THQ) for the three samples (Pb, Cd, Cr) did not exceed the limit (THQ>1). The computed Hazard Index (HI) was less than one, thus no adverse health effects are expected from exposure to the metals, and risk of getting disease from sample exposure is low. (50)
• Nephroprotective / L-NAME Induced Toxicity / Entire Plant: Study evaluated preventive effects of Eleusine indica aqueous extract (EIAE) against L-NAME induced renal damage in rats. Intraperitoneal L-NAME induced a significant increase in blood pressure, total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL-C and a significant reduction in HDL, with significant increase in creatinine, urea, and K, and reduction in GFR. Eleusine indica given simultaneously with L-NAME prevented the rise of blood pressure, improved lipid profile, kidney function and antioxidant defenses. Results showed nephroprotective effects and antioxidant capacities against kidney damage. (51)
• Anticancer Potential / Independent of Ras and Wnt Pathways / Leaves: Study evaluated the anticancer potential of E. indica methanolic leaf extract (EMLE) by focusing on two cancer-related pathways, Ras and Wnt pathways. using wild type and transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans strans. The EMLE did not affect the number of eggs laid and did not reduce Ras-mutant population demonstrating multi-vulva. Results suggest the anticancer potential may be independent of Ras and Wnt signaling pathways. (52)
• Anti-Trypanosomal / Leaves: Study evaluated 24 medicinal plant extracts for antiprotozoal activities against Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Antitrypanosomal assay showed ten extracts were active against T. brucei, with Eleusine indica displaying the most significant activity (IC50 and IC90 of 8.26 and 10.14 µg/mL). Study suggested bioassay guided fractionation and isolation of antitrypanosomal constituents. (54)
• Antiproliferative Against Cancer Cell Lines / Mechanisms / Roots: Study evaluated the anticancer effects of root fraction of E. indica (R-S5-C1-H1) on H1299, MCF-7, and SK-HEP-1 cell lines. Cell metabolic activity assays showed significantly reduced cell viability of the three cancer cell lines following treated with R-S5-C1-H1, with half-maximal inhibitory concentrations of 12.95, 15.99m and 13.69 µg/mL at 72h, respectively. Treated cells underwent apoptotic cell death. Apoptosis induction probably occurred through modulation of phospholipid synthesis and sphingolipid metabolism. The metabolomic profiling provides insights into the anticancer mechanisms of E. indica and elucidation of the molecular events following therapeutic interventions. (55)
• Antihypertensive / Whole Plant: Study evaluated evaluated the anti-hypertensive activity of powdered material of whole plant using in-vivo tail-cuff method in an adrenalin-induced hypertensive rat model. Hypertension was significantly inhibited by ethanol extract, and weakly inhibited by a chloroform extract. Previous studies have suggest that the antihypertensive effects could be due to flavonoids, glycoside, and phenolic compounds. (56)
• Cytotoxicity / Brine Shrimp Lethality Assay / Whole Plant: Study evaluated the potential cytotoxic properties of whole plant extracts (decoction, absolute ethanol, 50%water:50% ethanol) of Eleusine indica against brine shrimp nauplii. Best extraction method was 50:50 ethanol:water mixture, with LC50 of 153.99 ppm after 6 h exposure. Results suggest E. indica possesses cytotoxic behavior. Cytotoxicity was attributed to the secondary metabolites in the extract i.e., alkaloids, terpenes, flavonoids, tannins, anthraquinones, saponins, and cardiac glycosides. (57)
• Nanoparticles / Antibacterial / Leaves: Study reported on the synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Eleusine indica methanol extract of leaves as reducing agent. The AgNPs has predicted bactericidal activity according to ratio of MBC to MIC values against selected gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. (58)
Availability
Wild-crafted. |


![]()

