 Gen info Gen info
- Dendrobium Sw. is one of the largest genera in the orchidaceous family, which includes 900-2000 species.
- First described in 1799 by Olof Swartz and published in Heinrich Schrader's Journal für die Botanik.
(13)
- Specific epithet 'crumenatum' derives from Lain 'crumena' meaning 'leather moneybag.' (13)
Botany
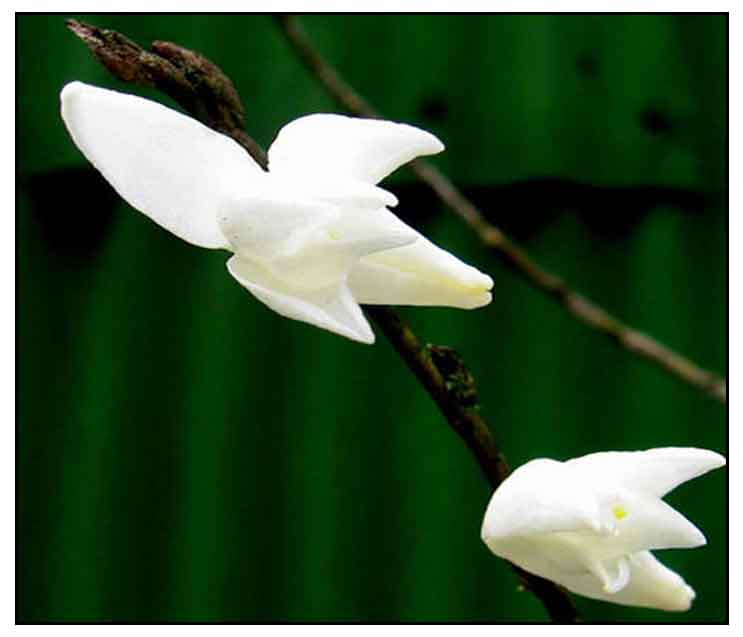
Pigeon denbrobium is an epiphytic orchid that grows on trees. Stems are slender, fascicled, smooth, elongated, up to 1 meter in length, with upright, sympodial pseudobulbs at the base, 8 to 12 centimeters long, about 2 centimeters thick. Leaves are scattered, distichous, oblong, 5 to 8 centimeters long and 1.5 to 2.5 centimeters wide, with a blunt tip. Flowers are pure white, fugacious, very fragrant, solitary or somewhat fascicled, appearing on the upper parts of the stems at the nodes; the center of the lip is pale yellow, 2.5 to 3 centimeters long. Fruits are capsular and elliptical, 2.2 centimeters long.
Distribution
- Native to the Philippines. (5)
-
Common and widely distributed orchid in the Philippines.
- Growing at sea level to an altitude of 500 meters.
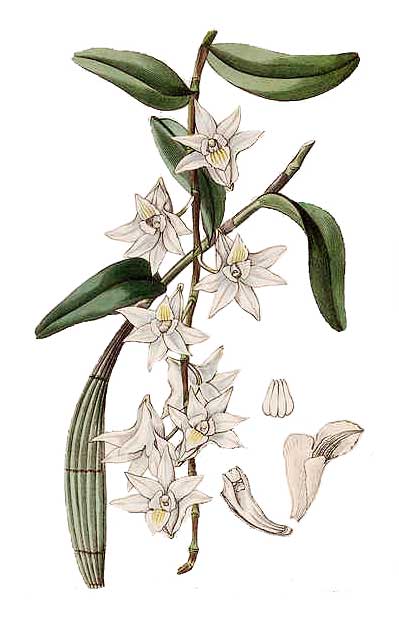 - One of the most common species of orchids in Asia. - One of the most common species of orchids in Asia.
- Also native to Andaman Is., Borneo, Cambodia, Christmas I., India, Jawa, Laos, Lesser Sunda Is., Malaya, Maluku, Myanmar, New Guinea, Nicobar Is., Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam.
(5)
Constituents
- Plant yields trace alkaloid in the pseudobulbs and leaves.
- Phytochemical study by Sandrasagara et al (2014) showed that bioactive compounds such as saponins, terpenoid, alkaloid, reducing sugar and flavonoid were present in most parts of D. crumenatum Terpenoid and reducing sugar were absent in leaves extract. Phlobatannins, anthraquinones, and tannins were not detected in any of the plant extracts.
(15)
Properties
- Studies have suggest antimicrobial, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant properties.
Parts used
Pseudobulbs and leaves.
Uses
Folkloric
- The Malays commonly used the juice of the pseudobulbs for treating ear infections. In Java, used similarly.
- Poultice of leaves used on boils and pimples.
- In Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam, plant used to remove impurities from the blood. In Malaysia, used to heal boils; juice from pseudobulbs used to relieve earache. (9) Poultice of leaves used to treat boils and pimples. (10)
- In Indonesia, pseudobulbs used to treat abscesses and boils, swelling in the outer ear; also to treat cholera. (11)
- Juice from swollen pseudobulbs used as ear drops to treat earache.
(12)
Others
- Crafts: Fibers from the stems are used as decorative material in basket making and other crafts.
- Rituals: In Malaysia, planted near house entrances as a good luck talisman to ward off evil spirits from entering. (12)
Studies
• Analgesic / Anti-Inflammatory / Antioxidant: Study of ethanol and methanol extracts showed anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive and antioxidant activities which may be related to the changes in the content of total alkaloids.(1)
• Reproductive Function Effects: Study evaluated the effect of pigeon orchid pseudobulb juice on female reproductive function using Wistar rats. Results showed a significant increase in estradiol level and increase in the number of tertiary follicles. (4)
• Antibacterial: In a study that evaluated nine plant samples for phytochemicals and biologic activity, Dendrobium crumenatum showed antifungal and antibacterial activity. (6)
• Antimicrobial / Stem, Root & Pseudo-bulbs: Study evaluated the potential antimicrobial activity of various parts of Dendrobium crumenatum against 8 pathogenic bacteria. The methanolic extract of stem, root, and pseudo-bulb exhibited antimicrobial activity comparable to standard antibiotics. Activity could be due to the presence of alkaloid and flavonoid compounds. (7)
• Frequency of Endophytic Fungi / Antimicrobial Activity: Study evaluated the frequency of endophytic fungi from roots, bulbs, stems, and leaves of D. crumenatum and its antimicrobial activity against Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, E. coli, B. subtilis, and S. aureus. Twelve species of fungi were isolated from 60 samples. Guignardia endophyllicola were the dominant endophytic fungi. Screening of anti-microorganism activity of the endophytic fungi showed inhibition of C. albicans and C. tropicalis, with no activity against B. subtilis, E. coli, and S. aureus. (8)
• Antimicrobial Endophytic Fungi: Endophytic microorganisms were found in the orchid Dendrobium crumenatum Sw. Fungi were isolated from roots, bulbouses, stems and leaves. Twelve species were identified from 60 samples. Guignardia endophyllicola Okane, Nakagiri and Ito were the dominant endophytic mould. Fusarium nivale (Fr.) Ces. inhibited Candida albicans and C. tropicalis. (14)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Gen info
Gen info - One of the most common species of orchids in Asia.
- One of the most common species of orchids in Asia.
