 Botany Botany
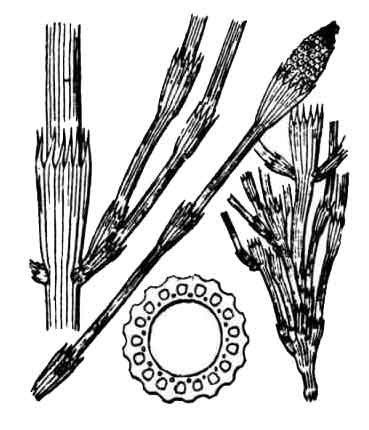
Sumbak is a fern ally with many hollow fluted aerial stems growing from perennial jointed and branched rootstocks. Roots are in whorls from the nodes. Fertile stems are erect, simple, 60 to 70 centimeters long, regularly striated, and more or less smooth. Leaves are much reduced, simple, united into a sheath at the nodes, their tips thinner and prolonged into teeth, somewhat funnel-shaped, 5 to 7 millimeters long. Spikes are 8 to 10 millimeters long, obtuse. Spores are in terminal cones.
Distribution
- Reported from Benguet Province in Luzon, in Bukidnon and Davao Provinces in Mindanao.
 Constituents Constituents
- Previous studies have isolated pinocembrin, chrysin, β-sitosterol, β-D- glycosylsitosterol, β-D-glucose, flavonoid glycosides and fatty acids12,13, flavonoid glycosides (kaempferol 3-O-sophoroside, kaempferol 3,7-O-β-D-diglucopyranoside, kaempferol 3-O-sophoroside-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, kaempferol 3-O-sophoroside and Caffeoyl-methylate-4-β-gluco-puranoside), megastigmane diglucoside (3S,5R,6S,7E,9S)- megastigman-7-ene-5,6-epoxy-3,9-diol 3,9-O-β-D-diglucopyranoside, (6R,9S)-3-oxo-a-ionol 9-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, (3S,5R,6R,7E,9S)-9-[(β-D-glucopyranosyl) oxy] megastigm-7- ene-3,5,6-triol), phenylethyl-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, (Z)-3-hexenyl-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, L-tryptophan14 and debilosides A-C; Blumenol A, corchoinoside C, sammangaoside A15.
- Study of whole plant yielded three new compounds, debilitriol (1), debilignanoside (2), and equisetumine (3), along with nine known compounds.
- Study of aqueous and n-hexane extracts of shade-dried stem and roots yielded carbohydrates, tannins, phenolic compounds, reducing sugar, fats and oils, anthraquinone glycosides, alkaloids, monosaccharides and saponin glycosides.
(15)
Properties
- Considered cooling, astringent, diuretic.
-
All species thought to contain alkaloids toxic to livestock.
- Studies have suggested hypolipidemic, radical scavenging, cytotoxic, antibacterial properties.
Parts used
Whole plant.
Uses
Folkloric
- In Malaysia, used for pains in the joints.
- In Africa, juice of E. debile taken orally to cure jaundice and hepatitis; also reported use as diuretic and treatment of kidney infections.
- Root paste used in the treatment of bones dislocation.
- In Nepal, paste from pounded plants applied to cure old ulcers. Root juice used for fever.
- In India, used for the treatment of urinary tract and kidney stones.
- In Bangladesh, used as cooling medicine; given for gonorrhea and bone fractures. Decoction of plant used for nasal polyps, various cancers (breast, liver, intestine, stomach, kidneys, and tongue.
- In the Rhe community In the Ba To district of central Vietnam, dried stems and leaves used for eye pain, back pain, and diabetes. (12)
- In North Sumatra, Indonesia, boiled leave used for treatment of kidney stones. (14)
- In the Gondia district of the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra, whole plant used as diuretic and for treatment of fever, gonorrhea, bone fractures, etc. (16)
- In Sikkim, Himalayas in India, aerial parts used on fresh wounds and nose bleeding to clot the blood. (17) In Manipur, India, whole plant used for gonorrhea and small pox.(18)
- In Manipur, India, ;whole plant crushed and mixed with Phogacanthus thyrsiformis used in the preparation of steam baths for treatment of arm and back pains.
(19)
Others
- Scouring / Polishing: High silica content of shoots provide a rough abrasive texture useful for scouring of cooking pots. In New Guinea, used to polish ornaments and smooth handles.
- Ethno-Veterinary: In the Himalayas. paste of stems and shoots applied externally to stop bleeding. Crush plant given twice daily with jaggery to livestock to treat blood in the urine and vaginal bleeding. (17)
Studies
• Hypolipidemic: Study showed E. debile Roxb alcohol extract decreased the triglyceride and total cholesterol of rat and triglyceride of rabbits. The concentration of b-apoprotein was not influenced. (3)
• Debilosides: Study isolated three new megastigmane glucosides from the whole plant of E. debile, with four known constituents - blumenol A, corchoinoside C, sammangaoside A and (3S,5R,6R,7E,9S)-9-[(β-d-glucopyranosyl)oxy]megastigm-7-ene-3,5,6-triol. (4)
• Cytotoxic / Antibacterial / Radical Scavenging Activity: Using brine shrimp lethality bioassay, n-hexane, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol extracts exhibited potent cytotoxic activity, suggesting antitumor or pesticidal activity. The EA extract showed significant free radical scavenging activity and an EA and n-butanol extract showed excellent antibacterial activity. (8)
• Cytotoxiity / Antioxidant: Study evaluated the bioactivity of various extracts of E. debile through Brine Shrimp Lethality Test (BSLT) and in vitro antioxidant assays i.e., total antioxidant capacity, DPPH radical scavenging activity, and total phenolics content. Resu9lts showed the chloroform extract to be most bioactive. The extract exhibited moderate toxicity against Artemisia nauplii with LC50 of 190.55 mg/L, along with highest antioxidant capacity (354.05 mg BHT eq/g sample and 330.30 mg ascorbic acid eq/g sample). The extract also showed remarkably higher phenolic content (713.72 mg gallic acid eq/g sample, with DPPH activity of 78.13%, and lowest EC50 of 295.02 mg/L. (10)
• Antihistaminic / Anticholinergic: Study of crude ethanolic and aqueous extracts of E. debile using isolated guinea pig ileum, rabbit jejunum, and rabbit trachea showed presence of antihistaminic and anticholergic activities. Results highlight its medicinal significant in the management of airway and gastrointestinal disorders. (11)
• Herniarin / Antioxidant / Anticholinergic: Study evaluated an ethanolic extract of whole plant for bioactive components. Fractions obtained after purification were analyzed for cytotoxicity by brine shrimp lethality assay and antioxidant properties using DPPH radical scavenging assay, total antioxidant capacity, and total phenolic content assays. The whole plant sample yielded herniarin. Study suggests E. debile can be a potential source of bioactive compounds. (13)
• Treatment of Hepatitis / Invention: Invention reports on the use of a Chinese medica preparation with total flavonoids of Equisetum ramosissimum, and the application of the preparation of medicines for treating hepatic diseases. The Chinese preparation with total flavonoids of Equisetum ramosissimum consists of 0.3-85% of the extract and 15-99.7% of a preparation of pharmaceutical adjuvants. The preparation claims advantages of promoting recovery of patients with hepatitis, lowering death rate, and reducing the onsel of liver cancer. (20)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Botany
Botany Constituents
Constituents