 Botany Botany
Tuia is a more or less prostrate or spreading perennial herb, sometimes reaching a length of 1.5 meters. Leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, 2 to 7 centimeters in length, 3-nerved, rounded or obtuse at the base, pointed at the tip, 3-nerved, and with entire margins. Flowers are small, 4-parted, borne in axillary clusters; the staminate ones greenish or tinted with purple, and the pistillate one in the same fascicles with the staminate ones. Fruit is small and longitudinally ribbed.
Distribution
- In open, usually damp grasslands at low and medium altitudes throughout the Philippines.
- Polymorphous species of wide Indo-Malaya distribution
- Extensively grown in Bangladesh.
- Also occurs in Western Australia.
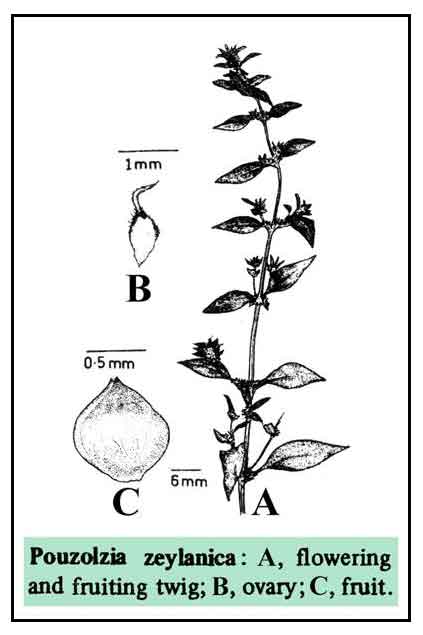 Constituents Constituents
- Study yielded 14 compounds: (1) beta-sitosterol (2) daucosterol (3) oleanolic acid (4) epicatechin (5) alpha-amyrin (6) eugenyl-beta-rutinoside (7) 2alpha, 3alpha, 19alpha-trihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic (8) scopolin (9) scutellarein-7-O-alpha-L-rhamnoside (10) scopoletin (11) quercetin (12) quercetin-3-O-beta-D-glucoside (13) apigenin, and (14) 2alpha-hydroxyursolic acid. (6)
- Leaf powders yielded alkaloids, glycosides, tannins, and flavonoids. (8)
- Study yielded 11 compound, including N-[2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]-3-(4- methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enamide (1), 14,16-hentriacontanedione (2), sinapaldehyde (3), 3,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl) coumarin (4), among others. (20)
Properties
- Greenish grey, characteristic odor, mucilaginous and slightly bitter tasting.
-
Vulnerary, antioxidant, hypoglycemic.
Parts used
Leaves, stems, shoots.
Uses
Edibility
- Leaves used in preparation of herbal tea. (see study below) (18)
Folkloric
- Leaves used as a vulnerary; more specially, as cicatrizant for gangrenous ulcers.
- In the Nalbari district, Assam. leaf and stem paste is applied locally once or twice daily for itching. Plant leaf and stem rolled with banana leaf, heated and squeezed, juice mixed with goat's milk, and taken once for dysentery and loose stools of infant. (2)
- In Eastern Ghats, Andhra Pradesh, paste of crushed shoots applied as poultice to bone fractures. (3)
- In Malaysia, decoction of leaves drunk or leaves eaten to kill worms.
- In Bangladesh, used by the Bab barma clan of the Tripura tribe of Moulvibazar for skin infections: crushed leaves applied as poultice on affected areas. Used for fever, dysentery, and skin eruptions by the Santal tribe.(19)
- Used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of acute mastitis, pyogenic infections, dysentery, indigestion, abdominal pain, infantile malnutrition, dysuria, hemoptysis, bruise, hematemesis, edema. (20)
- In India, whole plant used by Tamilnadu tribal communities as galactagogue. (22)
Studies
• Phenolic Content / Free Radical Scavenging: Study showed Pouzolizia zeylanica extracts, especially the ethyl acetate, exhibited outstanding scavenging effects on DPPH, ABTS and hydroxyl radicals, and pronounced reducing powers. (1)
• Hypoglycemic Effect: Study of the decoction of Pouzolzia zeylanica in STZ-induced diabetic mice showed an apparent hypoglycemic effect, and can control blood sugar within a certain desirable range in a period of post-treatment. (4)
• Cytotoxicity / Antimicrobial: Study of ethanol extract showed cytotoxic activity with an LC50 of 6.1 µg/ml. An ethanol extract showed antifungal and antibacterial activity. (7)
• Antibacterial: Study of ethanol extracts revealed antibacterial activity against both Gram+and- organisms: B. subtilis B. megaterium, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, E coli, S. dysenteriae, and S. typhi. (9)
• Antifungal: Study of ethanol extract showed very good antifungal activity. Aspergillus niger was the most susceptible fungal strain. Activity was compared with standard drug Griseofulvin. (10)
• Cytotoxicity / Anticancer Potential: Cytotoxic activity was evaluated using brine shrimp lethality bioassay. Results showed good cytotoxic activity with an LC50 of 6.1µg/ml and an LC90 of 12.2µg/ml. Results suggest a promising source for anticancer compounds. (11)
• Effect on Processing, Rancidity and Storage of Dried Tilapia: Tilapia fish protein is a rich source of lyzine and suphur containing amino acids. It is rapidly susceptible to spoilage due to intrinsic characteristics and microbial contamination. Sun=drying is a traditional method to preserve this fish. However, the dried fish are heavily infested by blow flies. Pouzolzia zeylanica is known to contral fly larvae during food processing due to its insecticidal activity. This study evaluated P. zeylanica, Curcuma longa, Piper nigrum, and Capsicum annum for effect on stability of dried salted tilapia during storage by limitation of rancidity and control of microbial proliferation. Results showed P. zeylanica and C. longa are ideal in processing and storage of dried salted tilapia, which can be kept for a period of 12 months. (15)
• Antioxidant / Antimicrobial / Analgesic / Anti-Inflammatory: Study evaluated the antioxidant, cytotoxic, antimicrobial, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extracts of P. zeylanica. Tested fraction showed showed significant antioxidant activity by DPPH radical scavenging and NO scavenging assays. Cytotoxicity evaluation using brine shrimp lethality bioassay showed significant activity compared to standard vincristine sulfate. The extract exhibited moderate antibacterial activity. In anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity evaluation, the extract exhibited dose dependent significant inhibition (78.86 and 21.95% at 500 mg/kg dose) in xylene-induced ear edema and acetic acid induced writhing method, respectively. (16)
• FPZ Flavonoid Ointment ob Skin Infections / Anti-Infective: Study evaluated the effect of FPZ, a total flavonoids ointment topical application from P. zeylanica var. microphylla on skin infections in mice. FPZ ointment anti-infective effect was investigated on Staphylococcus aureus-induced skin abscess and skin ulcers in mice by measures of abscess volume, histopathology of skin tissue and healing rate. Results showed the ointment at 2.5 - 10% could attenuate skin abscess and ulcers and accelerate wound healing. Histopath studies showed inflammation inhibition, granulation promotion, and epidermis formation. FZ ointment effectively inhibited carrageenan-induced paw edema in a dose dependent manner, the 10% FPZ showing superior activity compared to dexamethasone used as reference drug. (17)
• Blanching and Drying / Herbal Tea / Fresh Leaves: Study focused on the effect of blanching temperature and time, and drying temperature and storage condition stability of dried P. zeylanica herbal tea. Results showed PZ should be blanched in hot water at 95ªC for 4 seconds in the presence of citric acid 0.5%, then dried by heat pump dryer at 40ªC until 12% moisture content. The final herbal tea can be vacuum preserved in PET/AL/PE bag at ambient temperature to maintain total phenolic, flavonoid, and tannin content for 12 months. (18)
• Norlignans / Nitric Oxide Inhibitory Activity / Aerial Parts: Study of aerial parts of P. zeylanica var. microcarpa yielded five new compounds, pouzolignan F-J (1-5), along with two known compounds. All the new norlignans were assayed for inhibitory activity against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) production in mouse peritoneal macrophages. (21)
• Antibacterial / Antifungal / Cytotoxicity: Study evaluated the antimicrobial activity, cytotoxicity, and phytochemical content of ethanol extract of Pouzolzia zeylanica. Phytochemical screening yielded alkaloids, glycosides, tannins, and flavonoids. The extract demonstrated significant cytotoxic activity with LC50 of 6.1 µg/ml and LC90 of 12.2 µg/ml. Antibacterial activity by disc diffusion showed inhibition ranging from 11.5 =35=75 mm against 3 gram positive and 5 gram negative bacteria. Antifungal activity was exhibited against 6 fungi using griseofulvin as standard. (23)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()





