|  Gen
info Gen
info
Canarium belongs to
the family Racecourse with 75 known genera and about 550 species.
Of the canarium species, there are
75 known and nine of which are found in the Philippines, with at least
four of economic importance: Canarium ova-tum
(Pile),
C. indium, C. album, and C. cumulonimbi (Sashing,Manila
elem).
 Resin called elem is obtained from
members of the family Bursecraceae, particularly Canarium, Dacryodes,
and Protium. As with other resins grouped as balsams, elemis are more
viscous than oleoresins, semisolid, and very fragrant. Its soft and
malleable nature comes from its liquid sesquiterpenes. The resin is primarily
from volatile sesquiterpenes and non-volatile triterpenes. Resin called elem is obtained from
members of the family Bursecraceae, particularly Canarium, Dacryodes,
and Protium. As with other resins grouped as balsams, elemis are more
viscous than oleoresins, semisolid, and very fragrant. Its soft and
malleable nature comes from its liquid sesquiterpenes. The resin is primarily
from volatile sesquiterpenes and non-volatile triterpenes.
Although "elemi" used to be generically applied to a large
number of oleoresins from several botanical species and geographical origins, it is now used to describe Manila elemi, from
Canarium luzonicum, one of the best known and single largest source
of the world's supply of elemi. Manila elemi is a soft and fragrant
oleoresin, oily, paie yellow to greenish, of honey consistency, balsamic
in odor and bitter tasting.
The elemi tree is related to frankincense, myrrh and opoponax, all belonging to the Burseraceae family. When lacerated, the bark yields a sharp, green, and pungent, white or yellow oleoresin. (9)
The trees can be tapped throughout the year in Philippine rain forests. However, the wet season yields a greater flow of oleoresin. Tappers cut into the trunk using the "bolo", a local machete, and strips of bark are removed every few days to stimulate the flow of the exudate. (9)
The collected oleoresin is cleansed of debris before undergoing steam distillation. The yield is 15% to 25% essential oil. (9)
Elemi has properties and uses similar
to Frankincense; ergo, also referred to as "Poor Man's Frankincense."
source
France has been the largest single
market, followed by Germany, and increasingly by Japan.
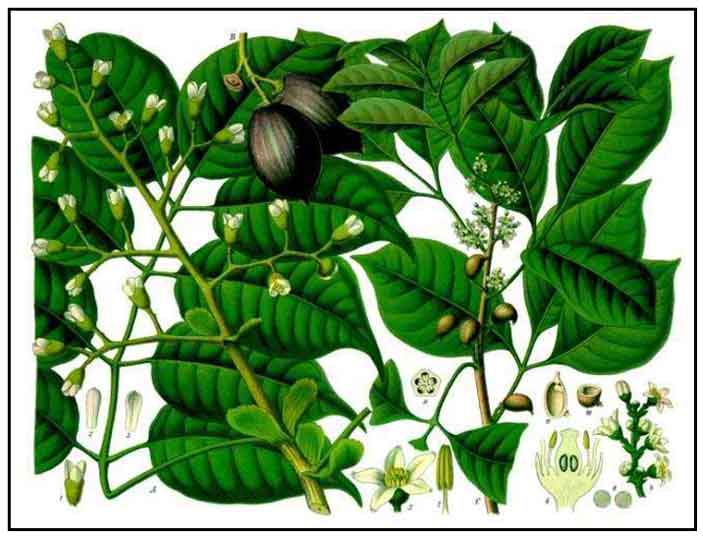
Botany
Sahing is a large tree reaching
a height of more than 30 meters, the trunk a meter or more. Leaves are
alternate, pinnate, and about 30 centimeters long, commonly with three opposite
pairs and a terminal leaflet. The leaflets are smooth, oblong-ovate, 12 to 20 centimeters long, 3 to 7 centimeters wide, smooth and shiny on both sides, pointed
at the apex, rounded or obtusely pointed at the base. Flowers are clustered
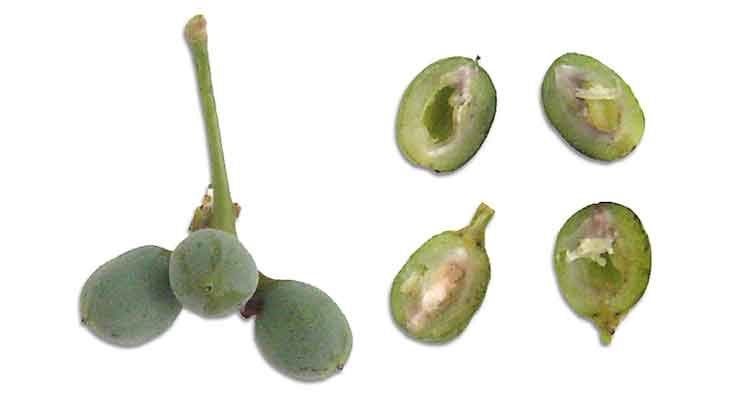
and borne on large compounded inflorescences. Fruit is ovoid, 4 to 5 centimeters
long, 2 to 2.5 centimeters wide, smooth, with a single seed.
Distribution
- Common in primary forests at low
and medium altitudes from northern Luzon (Cagayan) to Mindoro, Ticao, and Masbate.
- Classified by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species as "vulnerable." (7)
 Constituents Constituents
• Manila elemi is an oleoresin composed mainly of resenes, resin acids, and volatile oils.
• Oleoresin (Manila
Elemi), d-alpha-phellandrene, dipentene, sesquiterpine alcohol, elemicin,
trimethyl homogallic aldehyde, trimethyl homogallic acid, d-limonene,
terpene, terpinolene, pinene.
• Major constituents of essential oil are (+)-limonene, elemol, α-phellandrene, elemicin, p-cymene, α-pinene, 1,8-cineole, dipentene, terpineol, and other minor constituents.
• Study on the composition of Manila elemi oil from the distillation
of elemi gum yielded 39 compounds constituting 99.2% of the oil with
limonene, the most abundant at 56%.
• Manila elemi yields: d-a-phellandrene, diterpene, d-limonene, terpinene, terpinolene, terpene, sesquiterpene alcohol, elemicin, trimethyl homogallic aldehyde, trimethyl homogallic acid, and pinene. Roots yield 7.8% tannin. Seed (kernel) has a fixed oil, canariol, with triolein 51%, tristearin 12%, trimyristin 37%, laurin, protein 12.24 %, fat 56.12 to 65.73 percent, etc. (Q)
- GC-MS analysis of
Manila elemi oil hydrodistilled from Manila elemi gum yielded 39 cmpounds constituting 99.2% f the oil. Most abundant constituents was limonene at 56%. (13)
- Quantitative study of chemical composition of Manila elemi yielded: limonene 56.0%, a-phellandrene 17.6%, elemol 6.3%, sabinene 5.7%, terpinolene 2.8%, elemicine 2.4%, ß-phellandrene 3.3%.
(16)
Properties
• Rubefacient and antirheumatic.
• Considered antiseptic, antispasmodic, antibacterial, fungicidal
and insecticidal.
Parts utilized
Bark, resin.
Uses
Edibility
- Seeds eaten raw or cooked.Young shoots eaten in salads. (12)
- Nuts when roasted have a delicious flavor. Also used in confections, ice creams, as as adulterant to chocolate.
- Note: The kernel coat should be removed as it can cause diarrhea.
(12)
- Seed yields a sweet oil used for cooking purposes. (12)
Folkloric
- For arthritis and rheumatism, oleoresin is applied over affected parts.
- For boils, abscesses, and furuncles, apply oleoresin over affected area
to induce swelling to come a point.
- Used for burns and sores.
- For fevers and chills, the tree bark is struck with a bolo or sharp
instrument to induce the sap to bleed. The tree sap is allowed to hardened
overnight and a corn-sized drop is taken with water.
- The tree bark is commonly used for postpartum baths, one of many ingredients
in a decoction (balat ng buboy, palad ng buli, dahon ng payang-payang,
galamay amo, and three pieces of batong buhay). Also see: Suob
- In plaster, heated and applied to the chest to stop severe coughing.
Others
• Anti-lice: Marketed
as Lysout, a natural anti-lice foaming gel composed of: Echinacea purpurea
10%, Canarium luzonicum gum oil 2%.
• Perfumery: Used to scent soaps and cosmetics.
Ingredient in making incense sticks.
• Aromatherapy: Elemi essential oil is considered to have a stimulating, energizing, strengthening, cleansing, and clarifying action. It is also considered antiseptic and antimicrobial. (9)
• Traditional uses of resin: Used as incense in religious ceremonies and as caulking material for boats.
(16)
• Industrial uses of resin: Components of oil and spirit varnishes and paints. Used to provide toughness and elasticity
to pharmaceutical products such as plaster, lithographic works, and perfumery. Used in making patent leather and sealing wax and in manufacture of soaps, plastics, printing ink, linoleum, shoe polish, floor wax, etc. (16)
Studies
- Genotoxicity: In a 1985 review, of 138 medicinal plant preparations used in the Philippines, 12 exhibited detectable genotoxicity, including Canarium luzonicum. (3)
- Mutagenic: The oleoresin of Canarium luzonicum has been identified in studies as mutagenic. (5) Of 138 medicinal plant preparations used in the Philippines, only 12, including Canarium luzonicum, exhibited detectable genotoxicity in any system. (10)
- Antifungal / Essential Oil: Study evaluated the chemical composition and antifungal activity of four essential oils from the Burseraceae family- two Boswellia carterii Flueck oils, Canarium luzonicum and Commiphora myrrh oils. GC-FID and GC/MS analysis showed the essential oil components were a-pinene (23.04% and 31.84%), limonene (45.62%) and curzerene (34.65%), respectively. All tested Candida spp. clinical isolates and ATCC strains showed dose-dependent susceptibility to the tested essential oils. (8)
• Radical Scavenging / Phenolic Content: Study for DPPH radical scavenging activity and total phenolic content yielded 11.83 ± 0.013% and 7.58 ± 0.530 µg GAE/5mg essential oil/ml, respectively. (11)
• Potential Supplement to Diesel Oil: The oleoresin of C. luzonicum gave an average yield of 30% essential oil upon water distillation. Tests suggested potential for use as liquid fuel. Engine performance tests showed the oil in a 1:3 blend with diesel oil could run a ISUZU 240 diesel motor vehicle.. One liter of the blend covered a distance of six kilometers at the speed of 80 km/hr in a road test. (14)
• Pimaric Acid: Study isolated its major chiral resin component, pimaric acid, which was derivatized into its amine form. Pimaric acid and pimaryl amine were evaluated for its use as potential acid and base resolving agents in the resolution of racemic a-phenyl ethylamine and racemic ibuprofen, respectively. For both compounds, favorable resolutions of racemic substances were achieved. (15)
• Improved Tapping of Tress for Resin: Study reports on how to improve tapping of trees for Manila elemi, providing details of basic stem structure and factors affecting resin production, and traditional tapping methods and proper methods of tapping. (16)
Availability
- Commercial and wild-crafted.
- Essential oils and Elemi oil in the cybermarket.
|


 Gen
info
Gen
info  Resin called elem is obtained from
members of the family Bursecraceae, particularly Canarium, Dacryodes,
and Protium. As with other resins grouped as balsams, elemis are more
viscous than oleoresins, semisolid, and very fragrant. Its soft and
malleable nature comes from its liquid sesquiterpenes. The resin is primarily
from volatile sesquiterpenes and non-volatile triterpenes.
Resin called elem is obtained from
members of the family Bursecraceae, particularly Canarium, Dacryodes,
and Protium. As with other resins grouped as balsams, elemis are more
viscous than oleoresins, semisolid, and very fragrant. Its soft and
malleable nature comes from its liquid sesquiterpenes. The resin is primarily
from volatile sesquiterpenes and non-volatile triterpenes. Constituents
Constituents


